A frequency-dependent decoding mechanism for axonal length sensing
- PMID: 26257607
- PMCID: PMC4508512
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00281
A frequency-dependent decoding mechanism for axonal length sensing
Abstract
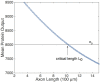
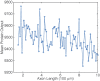
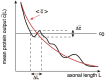
We have recently developed a mathematical model of axonal length sensing in which a system of delay differential equations describe a chemical signaling network. We showed that chemical oscillations emerge due to delayed negative feedback via a Hopf bifurcation, resulting in a frequency that is a monotonically decreasing function of axonal length. In this paper, we explore how frequency-encoding of axonal length can be decoded by a frequency-modulated gene network. If the protein output were thresholded, then this could provide a mechanism for axonal length control. We analyze the robustness of such a mechanism in the presence of intrinsic noise due to finite copy numbers within the gene network.
Keywords: axonal length control; biochemical oscillations; frequency decoding; gene network; intrinsic noise; protein thresholds.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

