Calm and smart? A selective review of meditation effects on decision making
- PMID: 26257700
- PMCID: PMC4513203
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01059
Calm and smart? A selective review of meditation effects on decision making
Abstract
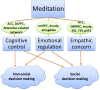
Over the past two decades, there has been a growing interest in the use of meditation to improve cognitive performance, emotional balance, and well-being. As a consequence, research into the psychological effects and neural mechanisms of meditation has been accumulating. Whether and how meditation affects decision making is not yet clear. Here, we review evidence from behavioral and neuroimaging studies and summarize the effects of meditation on social and non-social economic decision making. Research suggests that meditation modulates brain activities associated with cognitive control, emotion regulation and empathy, and leads to improved non-social and social decision making. Accordingly, we propose an integrative model in which cognitive control, emotional regulation, and empathic concern mediate the effects of meditation on decision making. This model provides insights into the mechanisms by which meditation affects the decision making process. More evidence is needed to test our explanatory model and to explore the function of specific brain areas and their interactive effects on decision making during meditation training.
Keywords: decision making; empathy; meditation; neuroimaging; prosocial behavior.
Figures
References
-
- Alfonso J. P., Caracuel A., Delgado-Pastor L. C., Verdejo-Garcia A. (2011). Combined goal management training and mindfulness meditation improve executive functions and decision-making performance in abstinent polysubstance abusers. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 117 78–81. 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2010.12.025 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Batson C. D., Ahmad N., Lishner D. A., Tsang J. (2011). “Empathy and altruism,” in The Oxford Handbook of Positive Psychology, eds Snyder C. R., Lopez S. J. (Oxford: Oxford University Press; ), 485–498.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

