Isolation and time lapse microscopy of highly pure hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 26258009
- PMCID: PMC4519541
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/417023
Isolation and time lapse microscopy of highly pure hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
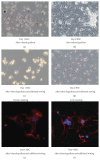
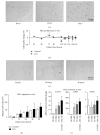
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are the main effector cells for liver fibrosis. We aimed at optimizing HSC isolation by an additional step of fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) via a UV laser. HSC were isolated from livers of healthy mice and animals subjected to experimental fibrosis. HSC isolation by iohexol- (Nycodenz) based density centrifugation was compared to a method with subsequent FACS-based sorting. We assessed cellular purity, viability, morphology, and functional properties like proliferation, migration, activation marker, and collagen expression. FACS-augmented isolation resulted in a significantly increased purity of stellate cells (>99%) compared to iohexol-based density centrifugation (60-95%), primarily by excluding doublets of HSC and Kupffer cells (KC). Importantly, this method is also applicable to young animals and mice with liver fibrosis. Viability, migratory properties, and HSC transdifferentiation in vitro were preserved upon FACS-based isolation, as assessed using time lapse microscopy. During maturation of HSC in culture, we did not observe HSC cell division using time lapse microscopy. Strikingly, FACS-isolated, differentiated HSC showed very limited molecular and functional responses to LPS stimulation. In conclusion, isolating HSC from mouse liver by additional FACS significantly increases cell purity by removing contaminations from other cell populations especially KC, without affecting HSC viability, migration, or differentiation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Optimized Isolation and Characterization of C57BL/6 Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells.Cells. 2022 Apr 19;11(9):1379. doi: 10.3390/cells11091379. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563686 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Culture of Primary Murine Hepatic Stellate Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1627:165-191. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7113-8_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28836201
-
Isolation and culture of hepatic stellate cells.Methods Mol Med. 2005;117:99-113. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-940-0:099. Methods Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16118448
-
Update on hepatic stellate cells: pathogenic role in liver fibrosis and novel isolation techniques.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Feb;6(1):67-80. doi: 10.1586/egh.11.92. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22149583 Review.
-
Wnt signaling in liver fibrosis: progress, challenges and potential directions.Biochimie. 2013 Dec;95(12):2326-35. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 24036368 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, Purification, and Culture of Primary Murine Hepatic Stellate Cells: An Update.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2669:1-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3207-9_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37247051
-
Optimization of the isolation procedure and culturing conditions for hepatic stellate cells obtained from mouse.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jan 29;41(1):BSR20202514. doi: 10.1042/BSR20202514. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33350435 Free PMC article.
-
Exceptional Uptake, Limited Protein Expression: Liver Macrophages Lost in Translation of Synthetic mRNA.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(9):e2409729. doi: 10.1002/advs.202409729. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39792811 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized Isolation and Characterization of C57BL/6 Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells.Cells. 2022 Apr 19;11(9):1379. doi: 10.3390/cells11091379. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563686 Free PMC article.
-
Single Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies Subsets of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Myofibroblasts in Liver Fibrosis.Cells. 2019 May 24;8(5):503. doi: 10.3390/cells8050503. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31137713 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

