Synthesis of lysine methyltransferase inhibitors
- PMID: 26258118
- PMCID: PMC4511967
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2015.00044
Synthesis of lysine methyltransferase inhibitors
Abstract
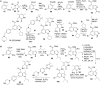
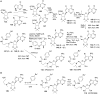
Lysine methyltransferase which catalyze methylation of histone and non-histone proteins, play a crucial role in diverse biological processes and has emerged as a promising target for the development of various human diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and psychiatric disorders. However, inhibiting lysine methyltransferases selectively has presented many challenges to medicinal chemists. During the past decade, lysine methyltransferase inhibitors covering many different structural classes have been designed and developed. In this review, we describe the development of selective, small-molecule inhibitors of lysine methyltransferases with an emphasis on their discovery and chemical synthesis. We highlight the current state of lysine methyltransferase inhibitors and discuss future directions and opportunities for lysine methyltransferase inhibitor discovery.
Keywords: S-adenosyl-l-methionine; epigenetics; inhibitors; lysine methyltransferase; synthesis.
Figures
















References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

