The pre-vertebrate origins of neurogenic placodes
- PMID: 26258298
- PMCID: PMC5008972
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14657
The pre-vertebrate origins of neurogenic placodes
Abstract
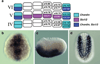
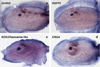
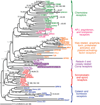
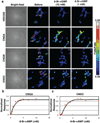
The sudden appearance of the neural crest and neurogenic placodes in early branching vertebrates has puzzled biologists for over a century. These embryonic tissues contribute to the development of the cranium and associated sensory organs, which were crucial for the evolution of the vertebrate "new head". A previous study suggests that rudimentary neural crest cells existed in ancestral chordates. However, the evolutionary origins of neurogenic placodes have remained obscure owing to a paucity of embryonic data from tunicates, the closest living relatives to those early vertebrates. Here we show that the tunicate Ciona intestinalis exhibits a proto-placodal ectoderm (PPE) that requires inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and expresses the key regulatory determinant Six1/2 and its co-factor Eya, a developmental process conserved across vertebrates. The Ciona PPE is shown to produce ciliated neurons that express genes for gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), a G-protein-coupled receptor for relaxin-3 (RXFP3) and a functional cyclic nucleotide-gated channel (CNGA), which suggests dual chemosensory and neurosecretory activities. These observations provide evidence that Ciona has a neurogenic proto-placode, which forms neurons that appear to be related to those derived from the olfactory placode and hypothalamic neurons of vertebrates. We discuss the possibility that the PPE-derived GnRH neurons of Ciona resemble an ancestral cell type, a progenitor to the complex neuronal circuit that integrates sensory information and neuroendocrine functions in vertebrates.
Figures






References
-
- Gaskell WH. The Origin of Vertebrates. Longmans, Green & Co; 1908.
-
- Gans C, Northcutt RG. Neural crest and the origin of vertebrates: a new head. Science. 1983;220:268–273. - PubMed
-
- Delsuc F, Brinkmann H, Chourrout D, Philippe H. Tunicates and not cephalochordates are the closest living relatives of vertebrates. Nature. 2006;439:965–968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

