Probing Gαi1 protein activation at single-amino acid resolution
- PMID: 26258638
- PMCID: PMC4876908
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3070
Probing Gαi1 protein activation at single-amino acid resolution
Abstract
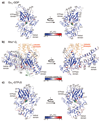
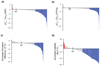
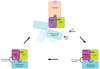
We present comprehensive maps at single-amino acid resolution of the residues stabilizing the human Gαi1 subunit in nucleotide- and receptor-bound states. We generated these maps by measuring the effects of alanine mutations on the stability of Gαi1 and the rhodopsin-Gαi1 complex. We identified stabilization clusters in the GTPase and helical domains responsible for structural integrity and the conformational changes associated with activation. In activation cluster I, helices α1 and α5 pack against strands β1-β3 to stabilize the nucleotide-bound states. In the receptor-bound state, these interactions are replaced by interactions between α5 and strands β4-β6. Key residues in this cluster are Y320, which is crucial for the stabilization of the receptor-bound state, and F336, which stabilizes nucleotide-bound states. Destabilization of helix α1, caused by rearrangement of this activation cluster, leads to the weakening of the interdomain interface and release of GDP.
Figures





References
-
- Gilman AG. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–49. - PubMed
-
- Wall MA, et al. The structure of the G protein heterotrimer Gi alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2. Cell. 1995;83:1047–58. - PubMed
-
- Sprang SR. G proteins, effectors and GAPs: structure and mechanism. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997;7:849–56. - PubMed
-
- Oldham WM, Van Eps N, Preininger AM, Hubbell WL, Hamm HE. Mechanism of the receptor-catalyzed activation of heterotrimeric G proteins. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2006;13:772–7. - PubMed
-
- Oldham WM, Hamm HE. Heterotrimeric G protein activation by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

