A gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data
- PMID: 26258848
- PMCID: PMC4552594
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3367
A gene-based association method for mapping traits using reference transcriptome data
Abstract
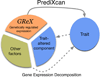
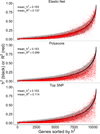
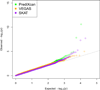
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified thousands of variants robustly associated with complex traits. However, the biological mechanisms underlying these associations are, in general, not well understood. We propose a gene-based association method called PrediXcan that directly tests the molecular mechanisms through which genetic variation affects phenotype. The approach estimates the component of gene expression determined by an individual's genetic profile and correlates 'imputed' gene expression with the phenotype under investigation to identify genes involved in the etiology of the phenotype. Genetically regulated gene expression is estimated using whole-genome tissue-dependent prediction models trained with reference transcriptome data sets. PrediXcan enjoys the benefits of gene-based approaches such as reduced multiple-testing burden and a principled approach to the design of follow-up experiments. Our results demonstrate that PrediXcan can detect known and new genes associated with disease traits and provide insights into the mechanism of these associations.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA165823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM061393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA139160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107666/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK20595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM092691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM61393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020065/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK20595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101820/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090937/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH094267/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007197/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA037844/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

