Heavy metal transport by the CusCFBA efflux system
- PMID: 26258953
- PMCID: PMC4622206
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2764
Heavy metal transport by the CusCFBA efflux system
Abstract
It is widely accepted that the increased use of antibiotics has resulted in bacteria with developed resistance to such treatments. These organisms are capable of forming multi-protein structures that bridge both the inner and outer membrane to expel diverse toxic compounds directly from the cell. Proteins of the resistance nodulation cell division (RND) superfamily typically assemble as tripartite efflux pumps, composed of an inner membrane transporter, a periplasmic membrane fusion protein, and an outer membrane factor channel protein. These machines are the most powerful antimicrobial efflux machinery available to bacteria. In Escherichia coli, the CusCFBA complex is the only known RND transporter with a specificity for heavy metals, detoxifying both Cu(+) and Ag(+) ions. In this review, we discuss the known structural information for the CusCFBA proteins, with an emphasis on their assembly, interaction, and the relationship between structure and function.
Keywords: CusCFBA efflux system; heavy metal resistance; multidrug resistance; resistance-nodulation-cell division.
© 2015 The Protein Society.
Figures


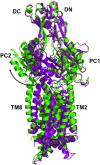
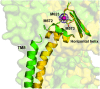




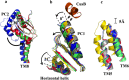



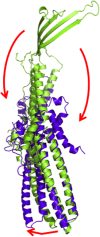
References
-
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. Geneva: WHO; 2014. . Available at: http://www.who.int/drugresistance/documents/surveillancereport/en/
-
- Higgins CF. Multiple molecular mechanisms for multidrug resistance transporters. Nature. 2007;446:749–757. - PubMed
-
- Silver S. Bacterial resistances to toxic metal ions division. Gene. 1996;179:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Saier MH., Jr Molecular phylogeny as a basis for the classification of transport proteins from bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. Adv Microb Physiol. 1998;40:81–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

