Fish oil and krill oil differentially modify the liver and brain lipidome when fed to mice
- PMID: 26260413
- PMCID: PMC4531896
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-015-0086-2
Fish oil and krill oil differentially modify the liver and brain lipidome when fed to mice
Abstract
Background: Marine food is an important source of omega-3 fatty acids with beneficial health effects. Oils from marine organisms have different fatty acid composition and differ in their molecular composition. Fish oil (FO) has a high content of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids mainly esterified to triacylglycerols, while in krill oil (KO) these fatty acids are mainly esterified to phospholipids. The aim was to study the effects of these oils on the lipid content and fatty acid distribution in the various lipid classes in liver and brain of mice.
Methods: Mice were fed either a high-fat diet (HF), a HF diet supplemented with FO or with KO (n = 6). After six weeks of feeding, liver and brain lipid extracts were analysed using a shotgun and TAG lipidomics approach. Student t-test was performed after log-transformation to compare differences between study groups.
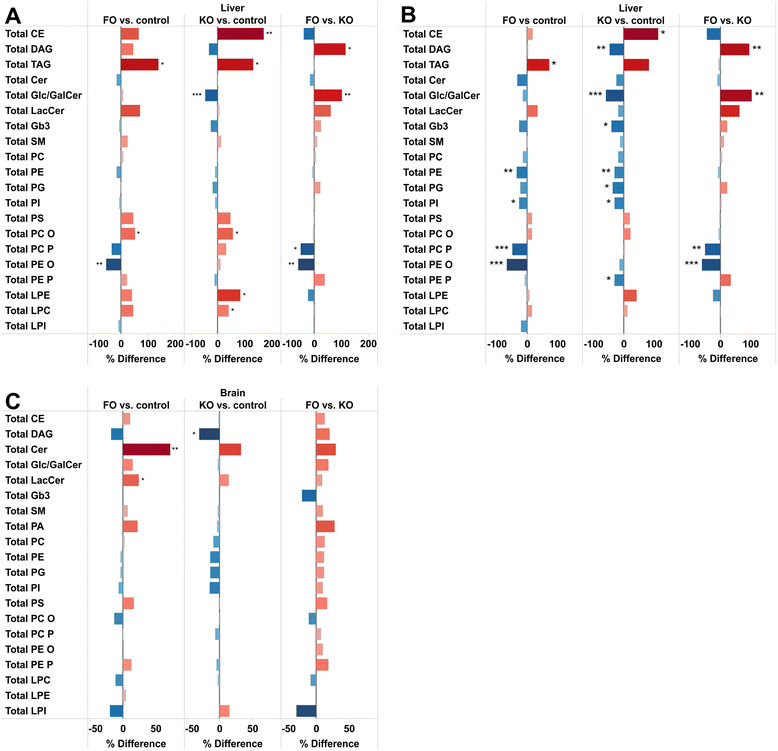
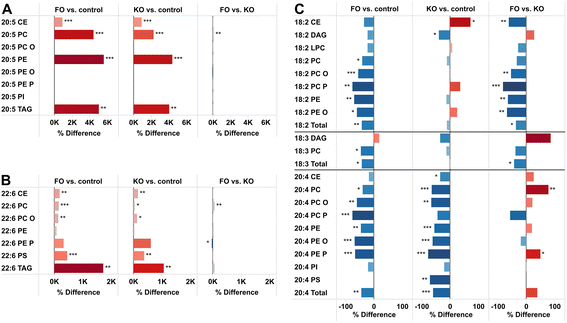
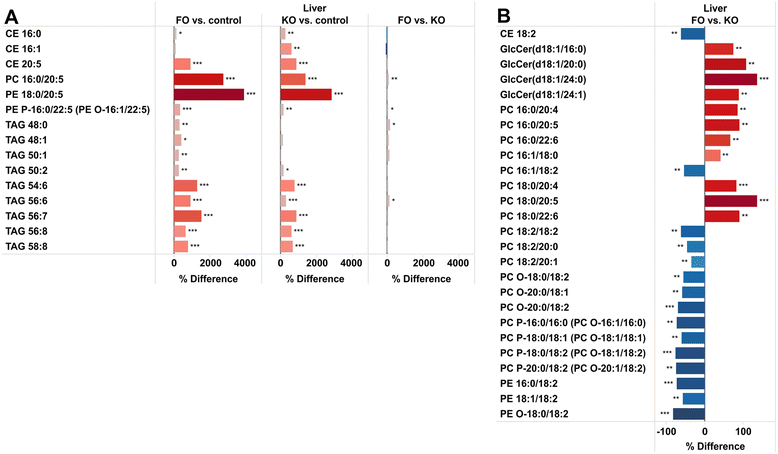
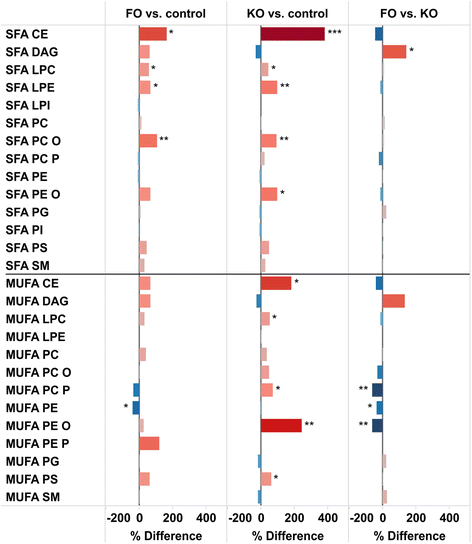
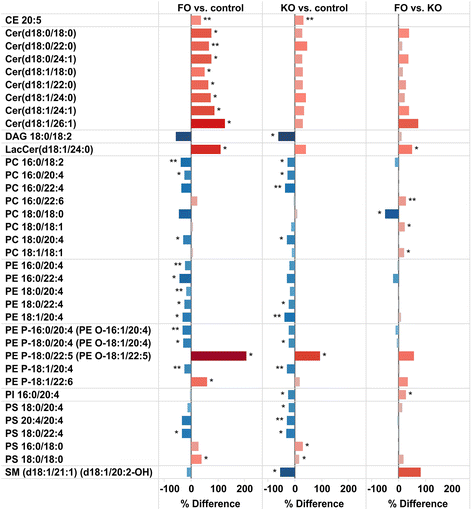
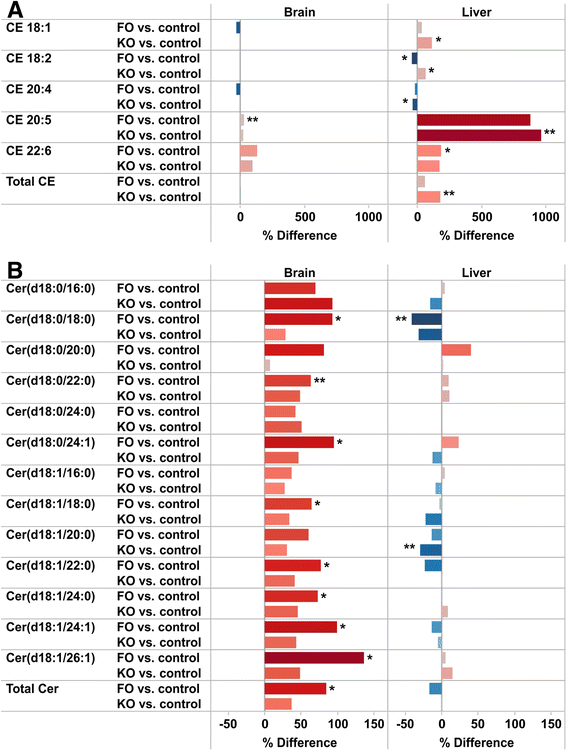
Results: Six weeks of feeding resulted in significant changes in the relative abundance of many lipid classes compared to control mice. In both FO and KO fed mice, the triacylglycerol content in the liver was more than doubled. The fatty acid distribution was affected by the oils in both liver and brain with a decrease in the abundance of 18:2 and 20:4, and an increase in 20:5 and 22:6 in both study groups. 18:2 decreased in all lipid classes in the FO group but with only minor changes in the KO group. Differences between the feeding groups were particularly evident in some of the minor lipid classes that are associated with inflammation and insulin resistance. Ceramides and diacylglycerols were decreased and cholesteryl esters increased in the liver of the KO group, while plasmalogens were decreased in the FO group. In the brain, diacylglycerols were decreased, more by KO than FO, while ceramides and lactosylceramides were increased, more by FO than KO.
Conclusion: The changes in the hepatic sphingolipids and 20:4 fatty acid levels were greater in the KO compared to the FO fed mice, and are consistent with a hypothesis that krill oil will have a stronger anti-inflammatory action and enhances insulin sensitivity more potently than fish oil.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Krill oil versus fish oil in modulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism in mice transgenic for TNF-α.Eur J Nutr. 2013 Jun;52(4):1315-25. doi: 10.1007/s00394-012-0441-2. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Eur J Nutr. 2013. PMID: 22923017
-
Fish oil and krill oil supplementations differentially regulate lipid catabolic and synthetic pathways in mice.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014 Apr 27;11:20. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-11-20. eCollection 2014. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014. PMID: 24834104 Free PMC article.
-
Absorption rate of krill oil and fish oil in blood and brain of rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 18;17(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0812-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30021606 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of bioavailability of krill oil versus fish oil and health effect.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2015 Aug 28;11:511-24. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S85165. eCollection 2015. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2015. PMID: 26357480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Krill and Fish Oil.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 30;26(15):7360. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157360. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An ω-3-enriched diet alone does not attenuate CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis.J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Dec;38:93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.08.010. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Nutr Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27732914 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Omega-3 PUFAs in Metabolic Disease Research: A Decade of Omics-Enabled Insights (2014-2024).Nutrients. 2025 May 28;17(11):1836. doi: 10.3390/nu17111836. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Resolution of Neuroinflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 13;10:1022. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01022. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31607902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Krill Oil Has Different Effects on the Plasma Lipidome Compared with Fish Oil Following 30 Days of Supplementation in Healthy Women: A Randomized Controlled and Crossover Study.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 13;12(9):2804. doi: 10.3390/nu12092804. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32933153 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiovascular and lipid-lowering effects of a marine lipoprotein extract in a high-fat diet-induced obesity mouse model.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Jan 22;20(3):292-306. doi: 10.7150/ijms.80727. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36860672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lemaitre-Delaunay D, Pachiaudi C, Laville M, Pousin J, Armstrong M, Lagarde M. Blood compartmental metabolism of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in humans after ingestion of a single dose of [13C]DHA in phosphatidylcholine. J Lipid Res. 1999;40:1867–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

