Peroxiredoxin 4 as an independent prognostic marker for survival in patients with early-stage lung squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 26261544
- PMCID: PMC4525878
Peroxiredoxin 4 as an independent prognostic marker for survival in patients with early-stage lung squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: Peroxiredoxin 4 (Prx 4) is a newly emerging antioxidant protein that has been studied in several human cancers. Recently, it was revealed that Prx 4 is highly expressed in human lung cancer and is needed for the promotion of lung cancer progression in vitro. However, there are no clinical data regarding the association of Prx 4 and prognosis in lung cancer.
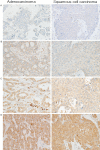
Materials and methods: The Prx 4 expression state as a prognostic indicator was assessed by immunohistochemical staining in 142 patients with stage II non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who had undergone curative surgery between 2006 and 2010. The association between the degree of Prx 4 expression and several clinicopathologic parameters was then evaluated by statistical analyses.
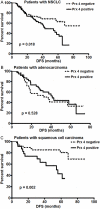
Results: The degree of Prx 4 expression was associated with histology and recurrence in the overall NSCLC patient group, with the proportion of patients with positive Prx 4 expression significantly higher for the adenocarcinoma subtype (39/70, 56%) than the squamous cell carcinoma subtype (23/72, 32%) (P = 0.004). However, when subgroup analyses according to histopathology were performed in terms of recurrence, positive Prx 4 expression was significantly correlated with higher recurrence rates (P = 0.003) and shorter disease-free survival (DFS) (P = 0.003, hazard ratio = 3.910) in patients with squamous cell carcinoma. In contrast, no meaningful relationship was observed between the level of Prx 4 expression and DFS in the adenocarcinoma subgroup.
Conclusion: Positive Prx 4 expression is significantly correlated with recurrence and shorter DFS in patients with early-stage lung squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Lung cancer; immunohistochemistry; peroxiredoxin.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society, Surveillance Research, 2013. Available at: http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@epidemiologysurveilance/docume.... Accessed May 20, 2014.
-
- Schiller JH, Harrinton D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J, Johnson DH. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Singhal S, Vachani A, Antin-Ozerkis D, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM. Prognostic implications of cell cycle, apoptosis, and angiogenesis biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer: a review. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3974–3986. - PubMed
-
- Mountain CF. Revisions in the International System for staging Lung cancer. Chest. 1997;111:1710–1717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
