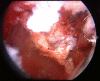
Endometrial tubal metaplasia in a young puerperal woman after breast cancer
- PMID: 26261678
- PMCID: PMC4526012
Endometrial tubal metaplasia in a young puerperal woman after breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Tamoxifen is the usual endocrine (anti-estrogen) therapy for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in pre and post-menopausal women. Previous studies have suggested an increased prevalence of endometrial diseases after treatment with tamoxifen.
Case presentation: The authors report a case of 38-year-old woman with diagnosis of endometrial polyp and tubal metaplasia, during puerperium and after micropapillary ductal breast cancer surgery, 5 years of tamoxifen treatment, spontaneous pregnancy without complications and full-term vaginal delivery.
Conclusion: Tamoxifen is a safe and reliable treatment of breast cancer, but data suggest an association with endometrial polyps, hyperplasia, metaplasia and carcinoma. One of the most common types of endometrial metaplasia is ciliated tubal metaplasia. It is generally known that endometrial tubal metaplasia is a benign disease. However studies propose endometrial tubal metaplasia to be a potential premalignant endometrial lesion and its association with endometrial hyperplasia and well-differentiated endometrioid carcinoma. We propose close monitoring of patients taking tamoxifen and prompt evaluation of any uterine bleeding or pelvic complaint or abnormal TVUS images.
Keywords: Breast cancer; endometrial polyp; tamoxifen; tubal metaplasia.
Figures
References
-
- Gallo MA, Kaufman D. Antagonistic and agonistic effects of tamoxifen: significance in human cancer. Semin Oncol. 1997;24(Suppl 1):S1-71–S1-80. - PubMed
-
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Tamoxifen Information: reducing the incidence of breast cancer in women at high risk. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on June 19, 2007. Retrieved July 3, 2007.
-
- Grilli S. Tamoxifen (TAM): the dispute goes on. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2006;42:170–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical