Distal Oblique Bundle Reinforcement for Treatment of DRUJ Instability
- PMID: 26261750
- PMCID: PMC4530179
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1556856
Distal Oblique Bundle Reinforcement for Treatment of DRUJ Instability
Abstract
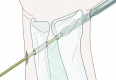
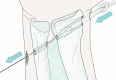
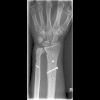
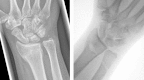
Background Chronic, dynamic bidirectional instability in the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) is diagnosed clinically, based on the patient's complaints and the finding of abnormal laxity in the vicinity of the distal ulna. In cases where malunion is ruled out or treated and there are no signs of osteoarthritis, stabilization of the DRUJ may offer relief. To this end, several different techniques have been investigated over the past 90 years. Materials and Methods In this article we outline the procedure for a new technique using a tendon graft to reinforce the distal edge of the interosseous membrane. Description of Technique A percutaneous technique is used to harvest the palmaris longus tendon and to create a tunnel, just proximal to the sigmoid notch, through the ulna and radius in an oblique direction. By overdrilling the radial cortex, the knotted tendon can be pulled through the radius and ulna and the knot blocked at the second radial cortex, creating a strong connection between the radius and ulna at the site of the distal oblique bundle (DOB). The tendon is fixed in the ulna with a small interference screw in full supination, preventing subluxation of the ulna out of the sigmoid notch during rotation. Results Fourteen patients were treated with this novel technique between 2011 and October 2013. The QuickDASH score at 25 months postoperatively (range 16-38 months) showed an improvement of 32 points. Similarly, an improvement of 33 points (67-34 months) was found on the PRWHE. Only one recurrence of chronic, dynamic bidirectional instability in the DRUJ was observed. Conclusion This simple percutaneous tenodesis technique between radius and ulna at the position of the distal edge of the interosseous membrane shows promise in terms of both restoring stability and relieving complaints related to chronic subluxation in the DRUJ.
Keywords: distal oblique bundle; distal radioulnar joint; instability; posttraumatic wrist disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Biomechanical Evaluation of the DRUJ After Distal Oblique Bundle Reconstruction.J Hand Surg Am. 2020 May;45(5):452.e1-452.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.10.011. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Hand Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 31870565
-
Stabilization of the distal radioulnar joint by reconstructing the interosseous membrane's distal oblique bundle: Cadaver study.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020 Dec;106(8):1581-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2020.03.041. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33082121
-
The Effect of Distal Radius Fracture Location on Distal Radioulnar Joint Stability: A Cadaveric Study.J Hand Surg Am. 2019 Jun;44(6):473-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Feb 15. J Hand Surg Am. 2019. PMID: 30777398
-
The distal interosseous membrane: current concepts in wrist anatomy and biomechanics.J Hand Surg Am. 2012 Jul;37(7):1501-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.04.037. J Hand Surg Am. 2012. PMID: 22721462 Review.
-
Does surgical reconstruction of the distal oblique bundle (DOB) provide similar stability as the intact bundle or Adams procedure? A systematic review.Ann Anat. 2023 Oct;250:152130. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2023.152130. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Ann Anat. 2023. PMID: 37467811
Cited by
-
Ulnar Wrist Deviation in Children With Obstetric Brachial Plexus Palsy: A Descriptive Study of Clinical and Radiological Findings of Impaired Ulnar Growth and Associated Incongruence of the Distal Radioulnar Joint.Hand (N Y). 2020 Sep;15(5):615-619. doi: 10.1177/1558944719831243. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Hand (N Y). 2020. PMID: 30819026 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous Suspensory Stabilization of Chronic Distal Radioulnar Joint (DRUJ) Dislocation Using an Adjustable Loop Endobutton Construct: Case Report.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2020 Sep 25;58(2):351-355. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1715515. eCollection 2023 Apr. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2020. PMID: 37252313 Free PMC article.
-
Distal Radioulnar Joint Instability: Diagnosis and Treatment.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2022 Jan;10(1):3-16. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2021.57194.2833. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2022. PMID: 35291239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing the Orientation of a Suture Button to Stabilize the Distal Radioulnar Joint in a Sawbones Model.J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2022 Aug 26;4(6):355-359. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsg.2022.06.007. eCollection 2022 Nov. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2022. PMID: 36425361 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomic Characteristics of the Distal Oblique Bundle of the Interosseous Membrane of the Forearm.Cureus. 2019 Jan 25;11(1):e3964. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3964. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 30956916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szabo R M. Distal radioulnar joint instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(4):884–894. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman R M, Jupiter J B. Instability of the distal radioulnar joint. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014;39(7):727–738. - PubMed
-
- Gofton W T, Gordon K D, Dunning C E, Johnson J A, King G J. Soft-tissue stabilizers of the distal radioulnar joint: an in vitro kinematic study. J Hand Surg Am. 2004;29(3):423–431. - PubMed
-
- Mohanti R C, Kar N. Study of triangular fibrocartilage of the wrist joint in Colles' fracture. Injury. 1980;11(4):321–324. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

