Myeloproliferative and thrombotic burden and treatment outcome of thrombocythemia and polycythemia patients
- PMID: 26261774
- PMCID: PMC4524819
- DOI: 10.5492/wjccm.v4.i3.230
Myeloproliferative and thrombotic burden and treatment outcome of thrombocythemia and polycythemia patients
Abstract
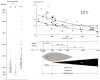
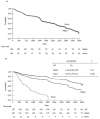
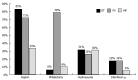
Prospective studies indicate that the risk of microvascular and major thrombosis in untreated thrombocythemia in various myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN-T) is not age dependent and causally related to platelet-mediated thrombosis in early, intermediate and advanced stages of thrombocythemia in MPN-T. If left untreated both microvascular and major thrombosis frequently do occur in MPN-T, but can easily be cured and prevented by low dose aspirin as platelet counts are above 350 × 10(9)/L. The thrombotic risk stratification in the retrospective Bergamo study has been performed in 100 essential thrombocythemia (ET) patients not treated with aspirin thereby overlooking the discovery in 1985 of aspirin responsive platelet-mediated arteriolar and arterial thrombotic tendency in MPN-T disease of ET and polycythemia vera (PV) patients. The Bergamo definition of high thrombotic risk and its persistence in the 2012 International Prognostic Score for ET is based on statistic mystification and not applicable for low and intermediate MPN-T disease burden in ET and PV patients on aspirin. With the advent of molecular screening of MPN patients, MPN-T disease associated with significant leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, constitutional symptoms and/or moderate splenomegaly are candidates for low dose peglyated interferon (Pegasys(R), 45 μg/mL once per week or every two weeks) as the first line myeloreductive treatment option in JAK2(V617F) mutated MPN-T disease in ET and PV patients. If non-responsive to or side effects induced by IFN, hydroxyurea is the second line myelosuppressive treatment option in JAK2(V617F) mutated ET and PV patients with increased MPN-T disease burden.
Keywords: Aspirin; Essential thrombocythemia; Hydroxyurea; Interferon; JAK2V617F mutation; Myeloproliferative neoplasms; Polycythemia vera.
Figures
References
-
- Michiels JJ. Erythromelalgia and thrombocythemia: Thesis Rotterdam. Rotterdam: Erasmus University Rotterdam; 1981. - PubMed
-
- van Genderen PJ, Michiels JJ. Erythromelalgic, thrombotic and haemorrhagic manifestations of thrombocythaemia. Presse Med. 1994;23:73–77. - PubMed
-
- Michiels JJ, Abels J, Steketee J, van Vliet HH, Vuzevski VD. Erythromelalgia caused by platelet-mediated arteriolar inflammation and thrombosis in thrombocythemia. Ann Intern Med. 1985;102:466–471. - PubMed
-
- Van Genderen PJ, Michiels JJ. Hydroxyurea in essential thrombocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:802–803. - PubMed
-
- van Genderen PJ, Mulder PG, Waleboer M, van de Moesdijk D, Michiels JJ. Prevention and treatment of thrombotic complications in essential thrombocythaemia: efficacy and safety of aspirin. Br J Haematol. 1997;97:179–184. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

