Landiolol, an ultra-short-acting β1-blocker, is useful for managing supraventricular tachyarrhythmias in sepsis
- PMID: 26261777
- PMCID: PMC4524822
- DOI: 10.5492/wjccm.v4.i3.251
Landiolol, an ultra-short-acting β1-blocker, is useful for managing supraventricular tachyarrhythmias in sepsis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether landiolol, an ultra-short-acting β1-antagonist, can safely and effectively control heart rate in septic patients with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
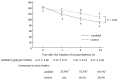
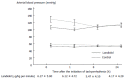
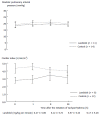
Methods: We reviewed all patients with sepsis who admitted to our intensive care unit between January 2006 and December 2011. Sixty one septic patients suffered from supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (heart rate ≥ 120 bpm for > 1 h). Among 61 patients, 39 patients were treated with landiolol (landiolol group) and 22 patients were not treated with landiolol (control group). Arterial pressure, heart rate, cardiac rhythm, pulmonary arterial pressure and cardiac output (if a pulmonary arterial catheter was inserted) were compared between the 2 groups at 1, 8 and 24 h after the initiation of tachyarrhythmias.
Results: Mean age and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment scores were similar between the 2 groups. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation/flutter (87%), paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (10%), and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (3%) were observed. The initial landiolol dose administered was 6.3 ± 5.8 g/kg per minute. Rapid and substantial reduction of heart rate was observed in the landiolol group without any deterioration of hemodynamics. Landiolol significantly reduced heart rate (from 145 ± 14 bpm to 90 ± 20 bpm) compared to the control group (from 136 ± 21 bpm to 109 ± 18 bpm, P < 0.05). The conversion to sinus rhythm was observed more frequently in the landiolol group than in the control group at every point (P < 0.01 at 8 h; P < 0.05 at 1 and 24 h).
Conclusion: Landiolol safely reduced heart rate and, in part, converted to sinus rhythm in septic patients with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Keywords: Conversion to sinus rhythm; Landiolol; Rate control; Sepsis; Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of landiolol, an ultra-short-acting β1-selective antagonist, for treatment of sepsis-related tachyarrhythmia (J-Land 3S): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Sep;8(9):863-872. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30037-0. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32243865 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of landiolol hydrochloride, an ultra-short-acting beta 1-selective blocker, on supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and flutter after pulmonary resection.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012 Aug;37(4):431-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2011.01315.x. Epub 2011 Nov 7. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012. PMID: 22059486
-
Effects of landiolol hydrochloride on intractable tachyarrhythmia after pediatric cardiac surgery.Ann Thorac Surg. 2013 May;95(5):1685-8. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.01.057. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23506630
-
Landiolol: A Review in Tachyarrhythmias.Drugs. 2018 Mar;78(3):377-388. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0883-9. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29470800 Review.
-
Intravenous Landiolol for Rate Control in Supraventricular Tachyarrhythmias in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 14;13(6):1683. doi: 10.3390/jcm13061683. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38541908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Landiolol for refractory tachyarrhythmias in the intensive care unit: case reports.Eur Heart J Suppl. 2022 Jun 13;24(Suppl D):D43-D49. doi: 10.1093/eurheartjsupp/suac026. eCollection 2022 Jun. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2022. PMID: 35706896 Free PMC article.
-
The role of beta-blocker drugs in critically ill patients: a SIAARTI expert consensus statement.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2023 Oct 23;3(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s44158-023-00126-2. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 37872608 Free PMC article.
-
Landiolol is effective for the treatment of tachycardia-induced cardiogenic shock in patients during septic shock therapy.BMJ Case Rep. 2017 Nov 1;2017:bcr2017222268. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-222268. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29092973 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis-induced Atrial Fibrillation: Can We Predict and Prevent This High-Risk Complication?Cureus. 2025 Jun 5;17(6):e85387. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85387. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40621331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Chronic Oral Beta-Blocker Intake on Intravenous Bolus Landiolol Response in Hospitalized Intensive Care Patients with Sudden-Onset Supraventricular Tachycardia-A Post Hoc Analysis of a Cross-Sectional Trial.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 20;16(6):839. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060839. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salman S, Bajwa A, Gajic O, Afessa B. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in critically ill patients with sepsis. J Intensive Care Med. 2008;23:178–183. - PubMed
-
- Leibovici L, Gafter-Gvili A, Paul M, Almanasreh N, Tacconelli E, Andreassen S, Nielsen AD, Frank U, Cauda R. Relative tachycardia in patients with sepsis: an independent risk factor for mortality. QJM. 2007;100:629–634. - PubMed
-
- Christian SA, Schorr C, Ferchau L, Jarbrink ME, Parrillo JE, Gerber DR. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of septic patients with new-onset atrial fibrillation. J Crit Care. 2008;23:532–536. - PubMed
-
- Jones SB, Romano FD. Plasma catecholamines in the conscious rat during endotoxicosis. Circ Shock. 1984;14:189–201. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

