p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT Signalling Cascades inParkinson's Disease
- PMID: 26261796
- PMCID: PMC4499569
p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT Signalling Cascades inParkinson's Disease
Abstract
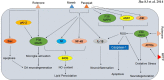
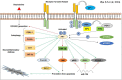
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative condition which has the second largest incidence rate among all other neurodegenerative disorders barring Alzheimer's disease (AD). Currently there is no cure and researchers continue to probe the therapeutic prospect in cell cultures and animal models of PD. Out of the several factors contributing to PD prognosis, the role of p38 MAPK (Mitogen activated protein-kinase) and PI3K/AKT signalling module in PD brains is crucial because the impaired balance between the pro- apoptotic and anti-apoptotic pathways trigger unwanted phenotypes such as microglia activation, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. These factors continue challenging the brain homeostasis in initial stages thereby essentially assisting the dopaminergic (DA) neurons towards progressive degeneration in PD. Neurotherapeutics against PD shall then be targeted against the misregulated accomplices of the p38 and PI3K/AKT cascades. In this review, we have outlined many such established mechanisms involving the p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways which can offer therapeutic windows for the rectification of aberrant DA neuronal dynamics in PD brains.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT; Parkinson’s disease (PD); apoptosis; neuroinflammation; neurotherapeutics; oxidative stress (OS); p38MAPK.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
PI3 k/akt inhibition induces apoptosis through p38 activation in neurons.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Apr;70(1):116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.01.007. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23376356
-
Neurotrophic Effect of Asiatic acid, a Triterpene of Centella asiatica Against Chronic 1-Methyl 4-Phenyl 1, 2, 3, 6-Tetrahydropyridine Hydrochloride/Probenecid Mouse Model of Parkinson's disease: The Role of MAPK, PI3K-Akt-GSK3β and mTOR Signalling Pathways.Neurochem Res. 2017 May;42(5):1354-1365. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2183-2. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28181071
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 acts via TβR-I on microglia to protect against MPP(+)-induced dopaminergic neuronal loss.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Jan;51:131-143. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 26254549
-
Nuclear factor-kappa β as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem. 2019 Jul;150(2):113-137. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14687. Epub 2019 Mar 26. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30802950 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple neuroprotective features of Scutellaria pinnatifida-derived small molecule.Heliyon. 2020 Aug 28;6(8):e04737. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04737. eCollection 2020 Aug. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32913905 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immune signatures in Parkinson's disease based on co-expression networks.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 17;14:1090382. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1090382. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36733342 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Play a Role in Parkinson's Disease by Regulating Microglia Function: From Pathogenetic Involvement to Therapeutic Potential.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jan 21;14:744942. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.744942. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35126050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FAK-Mediated Signaling Controls Amyloid Beta Overload, Learning and Memory Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 13;23(16):9055. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169055. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012331 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Unfolded Protein Response and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases with Special Focus on Prion Diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 May 1;9:120. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00120. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28507517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
