Dietary Patterns, Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Adults: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26262641
- PMCID: PMC4555139
- DOI: 10.3390/nu7085300
Dietary Patterns, Alcohol Consumption and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Adults: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Previous studies reported the potential associations between dietary patterns and the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) in adulthood, however a consistent perspective has not been established to date. Herein, we carried out this meta-analysis to evaluate the associations between dietary patterns and the risk of CHD. MEDLINE and EBSCO were searched for relevant articles published up to April 2015. A total of 35 articles (reporting 37 original studies) met the inclusion criteria and were included in the present meta-analysis. The decreased risk of CHD was shown for the highest compared with the lowest categories of healthy/prudent dietary patterns (odds ratio (OR) = 0.67; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.60, 0.75; p < 0.00001) and alcohol consumption (OR = 0.68; 95% CI: 0.59, 0.78; p < 0.00001). There was evidence of an increased risk of CHD in the highest compared with the lowest categories of the unhealthy/Western-type dietary patterns (OR = 1.45; 95% CI: 1.05, 2.01; p = 0.02). The results of this meta-analysis indicate that different dietary patterns may be associated with the risk of CHD.
Keywords: a meta-analysis; coronary heart disease; dietary patterns.
Figures
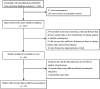
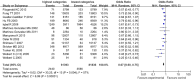
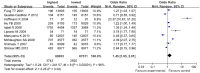
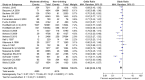
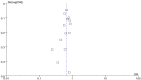
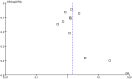
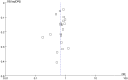
References
-
- Mackay J., Mensah G. The Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke. Available via World Health Organization. [(accessed on 29 September 2004)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/resources/atlas/en/
-
- Xu J., Lee E.T., Peterson L.E., Devereux R.B., Rhoades E.R., Umans J.G., Best L.G., Howard W.J., Paranilam J., Howard B.V. Differences in risk factors for coronary heart disease among diabetic and nondiabetic individuals from a population with high rates of diabetes: The Strong Heart Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012;97:3766–3767. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization World Health Statistics Annual, 2010. [(accessed on 13 June 2011)]. Available via World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/whosis/whostat/2010/en/index.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

