Genetic Ancestry and Asthma and Rhinitis Occurrence in Hispanic Children: Findings from the Southern California Children's Health Study
- PMID: 26263549
- PMCID: PMC4532441
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135384
Genetic Ancestry and Asthma and Rhinitis Occurrence in Hispanic Children: Findings from the Southern California Children's Health Study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Genetic Ancestry and Asthma and Rhinitis Occurrence in Hispanic Children: Findings from the Southern California Children's Health Study.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 25;10(9):e0139397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139397. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26406336 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Asthma and rhinitis are common childhood health conditions. Being an understudied and rapidly growing population in the US, Hispanic children have a varying risk for these conditions that may result from sociocultural (including acculturative factors), exposure and genetic diversities. Hispanic populations have varying contributions from European, Amerindian and African ancestries. While previous literature separately reported associations between genetic ancestry and acculturation factors with asthma, whether Amerindian ancestry and acculturative factors have independent associations with development of early-life asthma and rhinitis in Hispanic children remains unknown. We hypothesized that genetic ancestry is an important determinant of early-life asthma and rhinitis occurrence in Hispanic children independent of sociodemographic, acculturation and environmental factors.
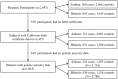
Methods: Subjects were Hispanic children (5-7 years) who participated in the southern California Children's Health Study. Data from birth certificates and questionnaire provided information on acculturation, sociodemographic and environmental factors. Genetic ancestries (Amerindian, European, African and Asian) were estimated based on 233 ancestry informative markers. Asthma was defined by parental report of doctor-diagnosed asthma. Rhinitis was defined by parental report of a history of chronic sneezing or runny or blocked nose without a cold or flu. Sample sizes were 1,719 and 1,788 for investigating the role of genetic ancestry on asthma and rhinitis, respectively.
Results: Children had major contributions from Amerindian and European ancestries. After accounting for potential confounders, per 25% increase in Amerindian ancestry was associated with 17.6% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.74-0.99) and 13.6% (95% CI: 0.79-0.98) lower odds of asthma and rhinitis, respectively. Acculturation was not associated with either outcome.
Conclusions: Earlier work documented that Hispanic children with significant contribution from African ancestry are at increased asthma risk; however, in Hispanic children who have little contribution from African ancestry, Amerindian ancestry was independently associated with lower odds for development of early-childhood asthma and rhinitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Asher MI, Montefort S, Bjorksten B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006;368(9537):733–43 ; 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69283-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

