Phospho-T356RB1 predicts survival in HPV-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- PMID: 26265441
- PMCID: PMC4662460
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4321
Phospho-T356RB1 predicts survival in HPV-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
Abstract
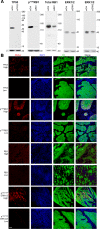
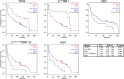
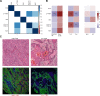
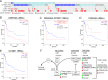
Locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) that is not associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) has a poor prognosis in contrast to HPV-positive disease. To better understand the importance of RB1 activity in HPV-negative SCCHN, we investigated the prognostic value of inhibitory CDK4/6 phosphorylation of RB1 on threonine 356 (T356) in archival HPV-negative tumor specimens from patients who underwent surgical resection and adjuvant radiation. We benchmarked pT356RB1 to total RB1, Ki67, pT202/Y204ERK1/2, and TP53, as quantified by automatic quantitative analysis (AQUA), and correlated protein expression with tumor stage and grade. High expression of pT356RB1 but not total RB1 predicted reduced overall survival (OS; P = 0.0295), indicating the potential relevance of post-translational phosphorylation. Paired analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data for regulators of this RB1 phosphorylation identified loss or truncating mutation of negative regulator CDKN2A (p16) and elevated expression of the CDK4/6 activator CCND1 (cyclin D) as also predicting poor survival. Given that CDK4/6 inhibitors have been most effective in the context of functional RB1 and low expression or deletion of p16 in other tumor types, these data suggest such agents may merit evaluation in HPV-negative SCCHN, specifically in cases associated with high pT356RB1.
Keywords: CDK4/6; E2F; RB1; biomarkers; head and neck cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGFR and RB1 as Dual Biomarkers in HPV-Negative Head and Neck Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Oct;15(10):2486-2497. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0243. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27507850 Free PMC article.
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Ambiguous human papillomavirus status, elevated p16, and deleted retinoblastoma 1.Head Neck. 2017 Mar;39(3):E34-E39. doi: 10.1002/hed.24604. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Head Neck. 2017. PMID: 27859938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Risk HPV, Biomarkers, and Outcome in Matched Cohorts of Head and Neck Cancer Patients Positive and Negative for HIV.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Feb;15(2):179-188. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0255. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27899422 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency and prognostic significance of p16(INK4A) protein overexpression and transcriptionally active human papillomavirus infection in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2015 Mar 17;112(6):1098-104. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.59. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25688737 Free PMC article.
-
HPV-Related Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2017;206:89-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43580-0_6. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27699531 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomics and advances towards precision medicine for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2017 Aug 22;2(5):310-319. doi: 10.1002/lio2.86. eCollection 2017 Oct. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 29094075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic insights into head and neck cancer.Cancers Head Neck. 2016;1:1. doi: 10.1186/s41199-016-0003-z. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Cancers Head Neck. 2016. PMID: 29034103 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR and RB1 as Dual Biomarkers in HPV-Negative Head and Neck Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Oct;15(10):2486-2497. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0243. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27507850 Free PMC article.
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Ambiguous human papillomavirus status, elevated p16, and deleted retinoblastoma 1.Head Neck. 2017 Mar;39(3):E34-E39. doi: 10.1002/hed.24604. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Head Neck. 2017. PMID: 27859938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling pathogenic mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes across head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients via next generation sequencing.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 15;13(12):6099-6112. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38187047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burtness B, Bauman JE, Galloway T. Novel targets in HPV-negative head and neck cancer: overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibition. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:e302–309. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Cracchiolo JR, Beck TN, et al. EGFR Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents in Head and Neck Cancer. In: Burtness B, Golemis EA, editors. Molecular Determinants of Head and Neck Cancer. New York: Springer; 2014.
-
- Seiwert TY, Beck TN, Salgia R. The Role of HGF/c-MET in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. In: Burtness B, Golemis EA, editors. Molecular Determinants of Head and Neck Cancer. New York: Springer; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

