Heat-Labile Enterotoxin IIa, a Platform To Deliver Heterologous Proteins into Neurons
- PMID: 26265718
- PMCID: PMC4542185
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00734-15
Heat-Labile Enterotoxin IIa, a Platform To Deliver Heterologous Proteins into Neurons
Abstract
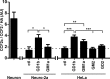
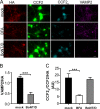
Cholera toxin (CT) and the related heat-labile enterotoxins (LT) of Escherichia coli have been implicated as adjuvants in human therapies, but reactivity upon intranasal delivery dampened efforts to develop other clinical applications. However, each CT family member variant has unique biological properties that may warrant development as therapeutic platforms. In the current study, a nontoxic variant of the heat-labile enterotoxin IIa (LTIIa) was engineered to deliver heterologous, functional proteins into the cytosol of neurons. As proof of principle, the LTIIa variant delivered two cargos into neurons. LTIIa delivered β-lactamase efficiently into cells containing complex gangliosides, such as GD1b, as host receptors. LTIIa delivery of β-lactamase was sensitive to brefeldin A, an inhibitor that collapses the Golgi compartment into the endoplasmic reticulum, but not sensitive to treatment with botulinum neurotoxin D (BoNT/D), an inhibitor of synaptic vesicle cycling. LTIIa delivered a single-chain, anti-BoNT/A camelid antibody that inhibited SNAP25 cleavage during post-BoNT/A exposure of neurons. Delivery of functional, heterologous protein cargos into neurons demonstrates the potential of LTII variants as platforms to deliver therapies to inactivate toxins and microbial infections and to reverse the pathology of human neurodegenerative diseases.
Importance: This study engineered a protein platform to deliver functional, heterologous proteins into neurons. The protein platform developed was a variant of the heat-labile enterotoxin IIa (LTIIa) which lacked the catalytic domain, yielding a nontoxic protein. As proof of principle, LTIIa variants delivered two functional proteins into neurons, β-lactamase and a camelid antibody. These studies show the utility of LTIIa variants to deliver therapies into neurons, which could be extended to inactivate toxins and microbial infections and potentially to reverse the progression of neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Copyright © 2015 Chen et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of receptor-mediated signal transduction by Escherichia coli type IIa heat-labile enterotoxin in the polarized human intestinal cell line T84.Infect Immun. 2001 Dec;69(12):7205-12. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7205-7212.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11705889 Free PMC article.
-
Mutants of type II heat-labile enterotoxin LT-IIa with altered ganglioside-binding activities and diminished toxicity are potent mucosal adjuvants.Infect Immun. 2007 Feb;75(2):621-33. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01009-06. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17118982 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the carbohydrate-binding specificities of cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins LTh-I, LT-IIa, and LT-IIb.Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1748-53. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1748-1753.1988. Infect Immun. 1988. PMID: 3290106 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-labile enterotoxin: beyond G(m1) binding.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Jun;2(6):1445-70. doi: 10.3390/toxins2061445. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Newly Identified Functions Associated With the Heat-Labile Toxin of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Aug 13;9:292. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00292. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31456954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering an AB5 Protein Carrier.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 23;8(1):12643. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30910-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30139944 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted intracellular delivery of Cas13 and Cas9 nucleases using bacterial toxin-based platforms.Cell Rep. 2022 Mar 8;38(10):110476. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110476. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35263584 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Inside of Cells with Biologicals: Toxin Routes in a Therapeutic Context.BioDrugs. 2023 Mar;37(2):181-203. doi: 10.1007/s40259-023-00580-y. Epub 2023 Feb 2. BioDrugs. 2023. PMID: 36729328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sortase-Modified Cholera Toxoids Show Specific Golgi Localization.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Apr 16;16(4):194. doi: 10.3390/toxins16040194. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668619 Free PMC article.
-
From GFP to β-lactamase: advancing intact cell imaging for toxins and effectors.Pathog Dis. 2015 Dec;73(9):ftv097. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv097. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26500183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gardlík R, Pálffy R, Hodosy J, Lukács J, Turna J, Celec P. 2005. Vectors and delivery systems in gene therapy. Med Sci Monit 11:RA110–RA121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

