Seasonal variation in muscle sympathetic nerve activity
- PMID: 26265752
- PMCID: PMC4562578
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12492
Seasonal variation in muscle sympathetic nerve activity
Abstract
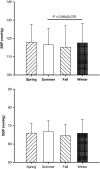
Epidemiologic data suggest there are seasonal variations in the incidence of severe cardiac events with peak levels being evident in the winter. Whether autonomic indices including muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) vary with season remains unclear. In this report, we tested the hypothesis that resting MSNA varies with the seasons of the year with peak levels evident in the winter. We analyzed the supine resting MSNA in 60 healthy subjects. Each subject was studied during two, three, or four seasons (total 237 visits). MSNA burst rate in the winter (21.0 ± 6.8 burst/min, mean ± SD) was significantly greater than in the summer (13.5 ± 5.8 burst/min, P < 0.001), the spring (17.1 ± 9.0 burst/min, P = 0.03), and the fall (17.9 ± 7.7 burst/min, P = 0.002). There was no significant difference in MSNA for other seasonal comparisons. The results suggest that resting sympathetic nerve activity varies along the seasons, with peak levels evident in the winter. We speculate that the seasonal changes in sympathetic activity may be a contribution to the previously observed seasonal variations in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; hemodynamic; nervous system; risk factors; sympathetic.
© 2015 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Alperovitch A, Lacombe JM, Hanon O, Dartigues JF, Ritchie K, Ducimetiere P, et al. Relationship between blood pressure and outdoor temperature in a large sample of elderly individuals: the Three-City study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009;169:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Ballaro A, Cortina-Borja M. Collin J. A seasonal variation in the incidence of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 1998;15:429–431. - PubMed
-
- Barnett AG, Sans S, Salomaa V, Kuulasmaa K, Dobson AJ. Project WM. The effect of temperature on systolic blood pressure. Blood Press. Monit. 2007;12:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Barretto AC, Santos AC, Munhoz R, Rondon MU, Franco FG, Trombetta IC, et al. Increased muscle sympathetic nerve activity predicts mortality in heart failure patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009;135:302–307. - PubMed
-
- Boulay F, Berthier F, Sisteron O, Gendreike Y. Gibelin P. Seasonal variation in chronic heart failure hospitalizations and mortality in France. Circulation. 1999;100:280–286. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

