A comparison of the biological effects of 125I seeds continuous low-dose-rate radiation and 60Co high-dose-rate gamma radiation on non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 26266801
- PMCID: PMC4534329
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133728
A comparison of the biological effects of 125I seeds continuous low-dose-rate radiation and 60Co high-dose-rate gamma radiation on non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the biological effects of 125I seeds continuous low-dose-rate (CLDR) radiation and 60Co γ-ray high-dose-rate (HDR) radiation on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells.
Materials and methods: A549, H1299 and BEAS-2B cells were exposed to 125I seeds CLDR radiation or 60Co γ-ray HDR radiation. The survival fraction was determined using a colony-forming assay. The cell cycle progression and apoptosis were detected by flow cytometry (FCM). The expression of the apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, cleaved-caspase-3, PARP, cleaved-PARP, BAX and Bcl-2 were detected by western blot assay.
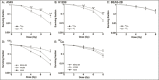
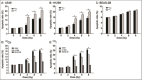
Results: After irradiation with 125I seeds CLDR radiation, there was a lower survival fraction, more pronounced cell cycle arrest (G1 arrest and G2/M arrest in A549 and H1299 cells, respectively) and a higher apoptotic ratio for A549 and H1299 cells than after 60Co γ-ray HDR radiation. Moreover, western blot assays revealed that 125I seeds CLDR radiation remarkably up-regulated the expression of Bax, cleaved-caspase-3 and cleaved-PARP proteins and down-regulated the expression of Bcl-2 proteins in A549 and H1299 cells compared with 60Co γ-ray HDR radiation. However, there was little change in the apoptotic ratio and expression of apoptosis-related proteins in normal BEAS-2B cells receiving the same treatment.
Conclusions: 125I seeds CLDR radiation led to remarkable growth inhibition of A549 and H1299 cells compared with 60Co HDR γ-ray radiation; A549 cells were the most sensitive to radiation, followed by H1299 cells. In contrast, normal BEAS-2B cells were relatively radio-resistant. The imbalance of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and the activation of caspase-3 and PARP proteins might play a key role in the anti-proliferative effects induced by 125I seeds CLDR radiation, although other possibilities have not been excluded and will be investigated in future studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
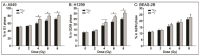


References
-
- Fidias P, Novello S. Strategies for prolonged therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.J ClinOncol.2010; 28:116–123. - PubMed
-
- Whitehurst AW, Bodemann BO, Cardenas J, Ferguson D, Girard L, Peyton M, et al. Synthetic lethal screen identification of chemosensitizer loci in cancer cells. Nature. 2007;446:815–819. - PubMed
-
- Ling CC, Li WX, Anderson LL. The relative biological effectiveness of I-125 and Pd-103. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;32:373–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

