A Hamster Model of Diet-Induced Obesity for Preclinical Evaluation of Anti-Obesity, Anti-Diabetic and Lipid Modulating Agents
- PMID: 26266945
- PMCID: PMC4534139
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135634
A Hamster Model of Diet-Induced Obesity for Preclinical Evaluation of Anti-Obesity, Anti-Diabetic and Lipid Modulating Agents
Abstract
Aim: Unlike rats and mice, hamsters develop hypercholesterolemia, and hypertriglyceridemia when fed a cholesterol-rich diet. Because hyperlipidemia is a hallmark of human obesity, we aimed to develop and characterize a novel diet-induced obesity (DIO) and hypercholesterolemia Golden Syrian hamster model.
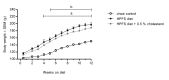
Methods and results: Hamsters fed a highly palatable fat- and sugar-rich diet (HPFS) for 12 weeks showed significant body weight gain, body fat accumulation and impaired glucose tolerance. Cholesterol supplementation to the diet evoked additional hypercholesterolemia. Chronic treatment with the GLP-1 analogue, liraglutide (0.2 mg/kg, SC, BID, 27 days), normalized body weight and glucose tolerance, and lowered blood lipids in the DIO-hamster. The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, linagliptin (3.0 mg/kg, PO, QD) also improved glucose tolerance. Treatment with peptide YY3-36 (PYY3-36, 1.0 mg/kg/day) or neuromedin U (NMU, 1.5 mg/kg/day), continuously infused via a subcutaneous osmotic minipump for 14 days, reduced body weight and energy intake and changed food preference from HPFS diet towards chow. Co-treatment with liraglutide and PYY3-36 evoked a pronounced synergistic decrease in body weight and food intake with no lower plateau established. Treatment with the cholesterol uptake inhibitor ezetimibe (10 mg/kg, PO, QD) for 14 days lowered plasma total cholesterol with a more marked reduction of LDL levels, as compared to HDL, indicating additional sensitivity to cholesterol modulating drugs in the hyperlipidemic DIO-hamster. In conclusion, the features of combined obesity, impaired glucose tolerance and hypercholesterolemia in the DIO-hamster make this animal model useful for preclinical evaluation of novel anti-obesity, anti-diabetic and lipid modulating agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-obesity effects of KR-66195, a synthetic DPP-IV inhibitor, in diet-induced obese mice and obese-diabetic ob/ob mice.Metabolism. 2014 Jun;63(6):793-9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.02.011. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24684824
-
Effects of liraglutide and sibutramine on food intake, palatability, body weight and glucose tolerance in the gubra DIO-rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Feb;33(2):194-200. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.168. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22301859 Free PMC article.
-
The DPP-IV inhibitor linagliptin and GLP-1 induce synergistic effects on body weight loss and appetite suppression in the diet-induced obese rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 15;741:254-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.08.010. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25160746
-
Obesity drugs in clinical development.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 Apr;7(4):312-8. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16625817 Review.
-
Drug combinations for dyslipidemia and obesity treatment in metabolic syndrome.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(29):3446-62. doi: 10.2174/138161209789105054. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19860690 Review.
Cited by
-
Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0.PLoS Biol. 2020 Jul 14;18(7):e3000411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 32663221 Free PMC article.
-
High Fat-High Fructose Diet-Induced Changes in the Gut Microbiota Associated with Dyslipidemia in Syrian Hamsters.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 20;12(11):3557. doi: 10.3390/nu12113557. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33233570 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma lipidomic analysis reveals strong similarities between lipid fingerprints in human, hamster and mouse compared to other animal species.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 26;8(1):15893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34329-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30367109 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine response and damages in the lungs of aging Syrian hamsters on a high-fat diet infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 14;14:1223086. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1223086. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520568 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Squalene in Cardiovascular Disease Risk-A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2020 Feb 5;12(2):414. doi: 10.3390/nu12020414. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32033387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384: 766–81. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999;282: 1523–9. - PubMed
-
- Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI, et al. Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature. 1996;379: 632–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

