Effects of age and cognition on a cross-cultural paediatric adaptation of the Sniffin' Sticks Identification Test
- PMID: 26267145
- PMCID: PMC4534354
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131641
Effects of age and cognition on a cross-cultural paediatric adaptation of the Sniffin' Sticks Identification Test
Abstract
Objectives: To study the effects of age and cognition on the performance of children aged 3 to 18 years on a culturally adapted version of the 16 item smell identification test from Sniffin' Sticks (SS16).
Methods: A series of pilots were conducted on 29 children aged 3 to 18 years old and 23 adults to produce an adapted version of the SS16 suitable for Brazilian children (SS16-Child). A final version was applied to 51 children alongside a picture identification test (PIT-SS16-Child) to access cognitive abilities involved in the smell identification task. In addition 20 adults performed the same tasks as a comparison group.
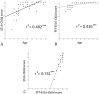
Results: The final adapted SS16-Child was applied to 51 children with a mean age of 9.9 years (range 3-18 years, SD=4.25 years), of which 68.3% were girls. There was an independent effect of age (p<0.05) and PIT-SS16-Child (p<0.001) on the performance on the SS16-Child, and older children reached the ceiling for scoring in the cognitive and olfactory test. Pre-school children had difficulties identifying items of the test.
Discussion/conclusions: A cross-culturally adapted version of the SS16 can be used to test olfaction in children but interpretation of the results must take age and cognitive abilities into consideration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adaptation of the Sniffin' Sticks Test in South-Kivu.Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2020 Dec;137(6):467-471. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2020.01.012. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2020. PMID: 32044270
-
The Influence of Cognitive Parameters on Olfactory Assessment in Healthy Children and Adolescents.Chem Senses. 2021 Jan 1;46:bjaa072. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjaa072. Chem Senses. 2021. PMID: 33119057
-
Cross-cultural application of the "Sniffin' Sticks" odor identification test.Am J Rhinol. 2007 Sep-Oct;21(5):570-3. doi: 10.2500/ajr.2007.21.3075. Am J Rhinol. 2007. PMID: 17999792
-
A Cross-Cultural Adaptation of the Sniffin' Sticks Olfactory Identification Test for US children.Chem Senses. 2017 Feb;42(2):133-140. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjw113. Epub 2016 Nov 20. Chem Senses. 2017. PMID: 28119356
-
Olfactory testing in children using objective tools: comparison of Sniffin' Sticks and University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test (UPSIT).J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Mar 1;44(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40463-015-0061-y. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015. PMID: 25890082 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Statistical overview of the Sniffin' sticks olfactory test from the perspectives of anosmia and hyposmia.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 15;15(1):8984. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93380-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40089590 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory assessment in the Chinese pediatric population.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Apr;97(16):e0464. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010464. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29668620 Free PMC article.
-
V Brazilian Consensus on Rhinitis - 2024.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jan-Feb;91(1):101500. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101500. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39388827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validation of the Connecticut olfactory test (CCCRC) adapted to Brazil.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Sep-Oct;88(5):725-732. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.09.013. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 33272838 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation and agreement of olfactory perception assessed by the Connecticut Chemosensory Clinical Research Center olfactory test and the Brief-Smell Identification Test.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Nov-Dec;88(6):858-866. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.11.013. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 33408061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Richman RA, Post EM, Sheehe PR, Wright HN. Olfactory performance during childhood. I. Development of an odorant identification test for children. J Pediatr. 1992;121: 908–911. - PubMed
-
- Kobal G, Klimek L, Wolfensberger M, Gudziol H, Temmel A, Owen CM, et al. Multicenter investigation of 1,036 subjects using a standardized method for the assessment of olfactory function combining tests of odor identification, odor discrimination, and olfactory thresholds. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000;257: 205–211. - PubMed
-
- Frank RA, Dulay MF, Gesteland RC. Assessment of the Sniff Magnitude Test as a clinical test of olfactory function. Physiol Behav. 2003;78: 195–204. - PubMed
-
- Frank R, Dulay M, Niergarth K, Gesteland R. A comparison of the sniff magnitude test and the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test in children and nonnative English speakers. Physiol Behav. 2004;81: 475–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

