Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: Factors Affecting Outcomes--A 10-year Experience at a Single Center
- PMID: 26267832
- PMCID: PMC4734163
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2015142489
Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: Factors Affecting Outcomes--A 10-year Experience at a Single Center
Abstract
Purpose: To identify predictors of oncologic outcomes after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of colorectal cancer liver metastases (CLMs) and to describe and evaluate a modified clinical risk score (CRS) adapted for ablation as a patient stratification and prognostic tool.
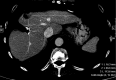
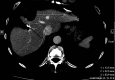
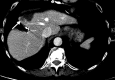
Materials and methods: This study consisted of a HIPAA-compliant institutional review board-approved retrospective review of data in 162 patients with 233 CLMs treated with percutaneous RFA between December 2002 and December 2012. Contrast material-enhanced CT was used to assess technique effectiveness 4-8 weeks after RFA. Patients were followed up with contrast-enhanced CT every 2-4 months. Overall survival (OS) and local tumor progression-free survival (LTPFS) were calculated from the time of RFA by using the Kaplan-Meier method. Log-rank tests and Cox regression models were used for univariate and multivariate analysis to identify predictors of outcomes.
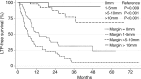
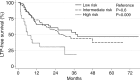
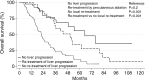
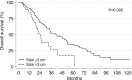
Results: Technique effectiveness was 94% (218 of 233). Median LTPFS was 26 months. At univariate analysis, predictors of shorter LTPFS were tumor size greater than 3 cm (P < .001), ablation margin size of 5 mm or less (P < .001), high modified CRS (P = .009), male sex (P = .03), and no history of prior hepatectomy (P = .04) or hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (P = .01). At multivariate analysis, only tumor size greater than 3 cm (P = .01) and margin size of 5 mm or less (P < .001) were independent predictors of shorter LTPFS. Median and 5-year OS were 36 months and 31%. At univariate analysis, predictors of shorter OS were tumor size larger than 3 cm (P = .005), carcinoembryonic antigen level greater than 30 ng/mL (P = .003), high modified CRS (P = .02), and extrahepatic disease (EHD) (P < .001). At multivariate analysis, tumor size greater than 3 cm (P = .006) and more than one site of EHD (P < .001) were independent predictors of shorter OS.
Conclusion: Tumor size of less than 3 cm and ablation margins greater than 5 mm are essential for satisfactory local tumor control. Tumor size of more than 3 cm and the presence of more than one site of EHD are associated with shorter OS.
© RSNA, 2015.
Figures




References
-
- Ruers T, Bleichrodt RP. Treatment of liver metastases, an update on the possibilities and results. Eur J Cancer 2002;38(7):1023–1033. - PubMed
-
- Norstein J, Silen W. Natural history of liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 1997;1(5):398–407. - PubMed
-
- Nordlinger B, Guiguet M, Vaillant JC, et al. . Surgical resection of colorectal carcinoma metastases to the liver: a prognostic scoring system to improve case selection, based on 1568 patients. Association Française de Chirurgie. Cancer 1996;77(7):1254–1262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

