Transcription Factor Repertoire of Homeostatic Eosinophilopoiesis
- PMID: 26268651
- PMCID: PMC4561201
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500510
Transcription Factor Repertoire of Homeostatic Eosinophilopoiesis
Abstract
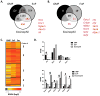
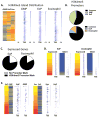
The production of mature eosinophils (Eos) is a tightly orchestrated process with the aim to sustain normal Eos levels in tissues while also maintaining low numbers of these complex and sensitive cells in the blood. To identify regulators of homeostatic eosinophilopoiesis in mice, we took a global approach to identify genome-wide transcriptome and epigenome changes that occur during homeostasis at critical developmental stages, including Eos-lineage commitment and lineage maturation. Our analyses revealed a markedly greater number of transcriptome alterations associated with Eos maturation (1199 genes) than with Eos-lineage commitment (490 genes), highlighting the greater transcriptional investment necessary for differentiation. Eos-lineage-committed progenitors (EoPs) were noted to express high levels of granule proteins and contain granules with an ultrastructure distinct from that of mature resting Eos. Our analyses also delineated a 976-gene Eos-lineage transcriptome that included a repertoire of 56 transcription factors, many of which have never previously been associated with Eos. EoPs and Eos, but not granulocyte-monocyte progenitors or neutrophils, expressed Helios and Aiolos, members of the Ikaros family of transcription factors, which regulate gene expression via modulation of chromatin structure and DNA accessibility. Epigenetic studies revealed a distinct distribution of active chromatin marks between genes induced with lineage commitment and genes induced with cell maturation during Eos development. In addition, Aiolos and Helios binding sites were significantly enriched in genes expressed by EoPs and Eos with active chromatin, highlighting a potential novel role for Helios and Aiolos in regulating gene expression during Eos development.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Lee J, Rosenberg HF. Eosinophils in health and disease. Elsevier/Academic Press; London; Waltham, MA: 2013.
-
- Mori Y, Iwasaki H, Kohno K, Yoshimoto G, Kikushige Y, Okeda A, Uike N, Niiro H, Takenaka K, Nagafuji K, Miyamoto T, Harada M, Takatsu K, Akashi K. Identification of the human eosinophil lineage-committed progenitor: revision of phenotypic definition of the human common myeloid progenitor. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2009;206:183–193. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duffin R, Leitch AE, Fox S, Haslett C, Rossi AG. Targeting granulocyte apoptosis: mechanisms, models, and therapies. Immunol Rev. 2010;236:28–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

