Increased Immune Response Variability during Simultaneous Viral Coinfection Leads to Unpredictability in CD8 T Cell Immunity and Pathogenesis
- PMID: 26269191
- PMCID: PMC4621125
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01432-15
Increased Immune Response Variability during Simultaneous Viral Coinfection Leads to Unpredictability in CD8 T Cell Immunity and Pathogenesis
Abstract
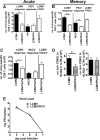
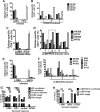
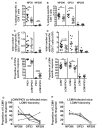
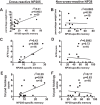
T cell memory is usually studied in the context of infection with a single pathogen in naive mice, but how memory develops during a coinfection with two pathogens, as frequently occurs in nature or after vaccination, is far less studied. Here, we questioned how the competition between immune responses to two viruses in the same naive host would influence the development of CD8 T cell memory and subsequent disease outcome upon challenge. Using two different models of coinfection, including the well-studied lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCMV) and Pichinde (PICV) viruses, several differences were observed within the CD8 T cell responses to either virus. Compared to single-virus infection, coinfection resulted in substantial variation among mice in the size of epitope-specific T cell responses to each virus. Some mice had an overall reduced number of virus-specific cells to either one of the viruses, and other mice developed an immunodominant response to a normally subdominant, cross-reactive epitope (nucleoprotein residues 205 to 212, or NP205). These changes led to decreased protective immunity and enhanced pathology in some mice upon challenge with either of the original coinfecting viruses. In mice with PICV-dominant responses, during a high-dose challenge with LCMV clone 13, increased immunopathology was associated with a reduced number of LCMV-specific effector memory CD8 T cells. In mice with dominant cross-reactive memory responses, during challenge with PICV increased immunopathology was directly associated with these cross-reactive NP205-specific CD8 memory cells. In conclusion, the inherent competition between two simultaneous immune responses results in significant alterations in T cell immunity and subsequent disease outcome upon reexposure.
Importance: Combination vaccines and simultaneous administration of vaccines are necessary to accommodate required immunizations and maintain vaccination rates. Antibody responses generally correlate with protection and vaccine efficacy. However, live attenuated vaccines also induce strong CD8 T cell responses, and the impact of these cells on subsequent immunity, whether beneficial or detrimental, has seldom been studied, in part due to the lack of known T cell epitopes to vaccine viruses. We questioned if the inherent increased competition and stochasticity between two immune responses during a simultaneous coinfection would significantly alter CD8 T cell memory in a mouse model where CD8 T cell epitopes are clearly defined. We show that some of the coinfected mice have sufficiently altered memory T cell responses that they have decreased protection and enhanced immunopathology when reexposed to one of the two viruses. These data suggest that a better understanding of human T cell responses to vaccines is needed to optimize immunization strategies.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Lam KS, Marshall ID. 1968. Dual infections of Aedes aegypti with arboviruses. I. Arboviruses that have no apparent cytopathic effect in the mosquito. Am J Trop Med Hyg 17:625–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI054455/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-077719/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI047140/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI046578/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-079665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK032520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI-046578/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-007349/PHS HHS/United States
- AI-054455/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047140/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI109858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI046629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-046629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007349/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK-032520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI077719/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-047140/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI077719/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

