Does kin selection moderate sexual conflict in Drosophila?
- PMID: 26269501
- PMCID: PMC4632634
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2015.1417
Does kin selection moderate sexual conflict in Drosophila?
Abstract
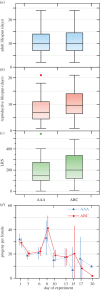
Two recent studies provide provocative experimental findings about the potential influence of kin recognition and cooperation on the level of sexual conflict in Drosophila melanogaster. In both studies, male fruit flies apparently curbed their mate-harming behaviours in the presence of a few familiar or related males, suggesting some form of cooperation mediated by kin selection. In one study, the reduction in agonistic behaviour by brothers apparently rendered them vulnerable to dramatic loss of paternity share when competing with an unrelated male. If these results are robust and generalizable, fruit flies could be a major new focus for the experimental study of kin selection and social evolution. In our opinion, however, the restrictive conditions required for male cooperation to be adaptive in this species make it unlikely to evolve. We investigated these phenomena in two different populations of D. melanogaster using protocols very similar to those in the two previous studies. Our experiments show no evidence for a reduction in mate harm based upon either relatedness or familiarity between males, and no reduction in male reproductive success when two brothers are in the presence of an unfamiliar, unrelated, 'foreign' male. Thus, the reduction of sexual conflict owing to male cooperation does not appear to be a general feature of the species, at least under domestication, and these contrasting results call for further investigation: in new populations, in the field and in the laboratory populations in which these phenomena have been reported.
Keywords: Drosophila; cooperation; familiarity; kin selection; mate harm; sexual conflict.
© 2015 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Lessells CM. 1999. Sexual conflict in animals. In Levels of selection in evolution (ed. Keller L.), pp. 75–99. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
-
- Morrow EH, Arnqvist G, Pitnick S. 2003. Adaptation versus pleiotropy: why do males harm their mates? Behav. Ecol. 14, 802–806. (doi:10.1093/beheco/arg073) - DOI
-
- Hamilton WD. 1964. The genetical evolution of social behaviour, I and II. J. Theor. Biol. 7, 1–52. (doi:10.1016/0022-5193(64)90038-4) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taylor PD. 1992. Altruism in viscous populations: an inclusive fitness model. Evol. Ecol. 6, 352–356. (doi:10.1007/BF02270971) - DOI
-
- Pizzari T, Biernaskie JM, Carazo P. 2014. Inclusive fitness and sexual conflict: how population structure can modulate the battle of the sexes. BioEssays 37, 155–166. (doi:10.1002/bies.201400130) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

