Real-Time Imaging Reveals Local, Transient Vascular Permeability, and Tumor Cell Intravasation Stimulated by TIE2hi Macrophage-Derived VEGFA
- PMID: 26269515
- PMCID: PMC4560669
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0012
Real-Time Imaging Reveals Local, Transient Vascular Permeability, and Tumor Cell Intravasation Stimulated by TIE2hi Macrophage-Derived VEGFA
Abstract
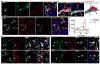
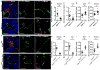
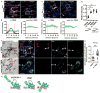
Dissemination of tumor cells is an essential step in metastasis. Direct contact between a macrophage, mammalian-enabled (MENA)-overexpressing tumor cell, and endothelial cell [Tumor MicroEnvironment of Metastasis (TMEM)] correlates with metastasis in breast cancer patients. Here we show, using intravital high-resolution two-photon microscopy, that transient vascular permeability and tumor cell intravasation occur simultaneously and exclusively at TMEM. The hyperpermeable nature of tumor vasculature is described as spatially and temporally heterogeneous. Using real-time imaging, we observed that vascular permeability is transient, restricted to the TMEM, and required for tumor cell dissemination. VEGFA signaling from TIE2(hi) TMEM macrophages causes local loss of vascular junctions, transient vascular permeability, and tumor cell intravasation, demonstrating a role for the TMEM within the primary mammary tumor. These data provide insight into the mechanism of tumor cell intravasation and vascular permeability in breast cancer, explaining the value of TMEM density as a predictor of distant metastatic recurrence in patients.
Significance: Tumor vasculature is abnormal with increased permeability. Here, we show that VEGFA signaling from TIE2(hi) TMEM macrophages results in local, transient vascular permeability and tumor cell intravasation. These data provide evidence for the mechanism underlying the association of TMEM with distant metastatic recurrence, offering a rationale for therapies targeting TMEM.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
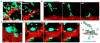
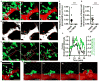
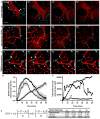
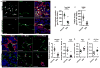
Comment in
-
Cancer Metastasis: Perivascular Macrophages Under Watch.Cancer Discov. 2015 Sep;5(9):906-8. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0819. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 26334045
References
-
- Yuan F, Dellian M, Fukumura D, Leunig M, Berk DA, Torchilin VP, et al. Vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft: molecular size dependence and cutoff size. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3752–6. - PubMed
-
- Gerlowski LE, Jain RK. Microvascular permeability of normal and neoplastic tissues. Microvasc Res. 1986;31:288–305. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak HF, Dvorak AM, Manseau EJ, Wiberg L, Churchill WH. Fibrin gel investment associated with line 1 and line 10 solid tumor growth, angiogenesis, and fibroplasia in guinea pigs. Role of cellular immunity, myofibroblasts, microvascular damage, and infarction in line 1 tumor regression. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1979;62:1459–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

