CXCR4 Protein Epitope Mimetic Antagonist POL5551 Disrupts Metastasis and Enhances Chemotherapy Effect in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26269605
- PMCID: PMC4784694
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0252
CXCR4 Protein Epitope Mimetic Antagonist POL5551 Disrupts Metastasis and Enhances Chemotherapy Effect in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
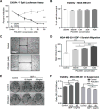
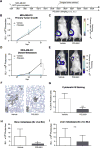
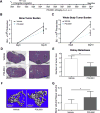
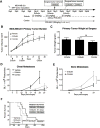
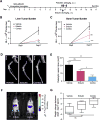
The SDF-1 receptor CXCR4 has been associated with early metastasis and poorer prognosis in breast cancers, especially the most aggressive triple-negative subtype. In line with previous reports, we found that tumoral CXCR4 expression in patients with locally advanced breast cancer was associated with increased metastases and rapid tumor progression. Moreover, high CXCR4 expression identified a group of bone marrow-disseminated tumor cells (DTC)-negative patients at high risk for metastasis and death. The protein epitope mimetic (PEM) POL5551, a novel CXCR4 antagonist, inhibited binding of SDF-1 to CXCR4, had no direct effects on tumor cell viability, but reduced migration of breast cancer cells in vitro. In two orthotopic models of triple-negative breast cancer, POL5551 had little inhibitory effect on primary tumor growth, but significantly reduced distant metastasis. When combined with eribulin, a chemotherapeutic microtubule inhibitor, POL5551 additively reduced metastasis and prolonged survival in mice after resection of the primary tumor compared with single-agent eribulin. Hypothesizing that POL5551 may mobilize tumor cells from their microenvironment and sensitize them to chemotherapy, we used a "chemotherapy framing" dosing strategy. When administered shortly before and after eribulin treatment, three doses of POL5551 with eribulin reduced bone and liver tumor burden more effectively than chemotherapy alone. These data suggest that sequenced administration of CXCR4 antagonists with cytotoxic chemotherapy synergize to reduce distant metastases.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
POL5551 compound was provided by Polyphor Ltd. Targeted funding to purchase NSG mice for a subset of experiments was provided by Polyphor Ltd. GD, BR, GT, EC, MB, JZ and KD are all employed by Polyphor and own shares in the company.
Figures
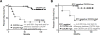
References
-
- Teicher BA, Fricker SP. CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2010;16:2927–31. - PubMed
-
- Dar A, Kollet O, Lapidot T. Mutual, reciprocal SDF-1/CXCR4 interactions between hematopoietic and bone marrow stromal cells regulate human stem cell migration and development in NOD/SCID chimeric mice. Experimental hematology. 2006;34:967–75. - PubMed
-
- Ma Q, Jones D, Borghesani PR, Segal RA, Nagasawa T, Kishimoto T, et al. Impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, and derailed cerebellar neuron migration in CXCR4- and SDF-1-deficient mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95:9448–53. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nagasawa T, Hirota S, Tachibana K, Takakura N, Nishikawa S, Kitamura Y, et al. Defects of B-cell lymphopoiesis and bone-marrow myelopoiesis in mice lacking the CXC chemokine PBSF/SDF-1. Nature. 1996;382:635–8. - PubMed
-
- Ara T, Tokoyoda K, Sugiyama T, Egawa T, Kawabata K, Nagasawa T. Long-term hematopoietic stem cells require stromal cell-derived factor-1 for colonizing bone marrow during ontogeny. Immunity. 2003;19:257–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 CA094056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA113275/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA174096/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA100730/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA154737/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027552/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA167540/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA182333/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA142750/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA170198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1F31CA174096-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA172623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA170198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA142750/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154737/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K12CA167540/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 CA097250/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097250/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK52574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA182333/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR057235/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA94056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA100730/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA097250/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

