Surveillance for Waterborne Disease Outbreaks Associated with Drinking Water - United States, 2011-2012
- PMID: 26270059
- PMCID: PMC4584589
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6431a2
Surveillance for Waterborne Disease Outbreaks Associated with Drinking Water - United States, 2011-2012
Abstract
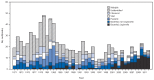
Advances in water management and sanitation have substantially reduced waterborne disease in the United States, although outbreaks continue to occur. Public health agencies in the U.S. states and territories* report information on waterborne disease outbreaks to the CDC Waterborne Disease and Outbreak Surveillance System (http://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/surveillance/index.html). For 2011-2012, 32 drinking water-associated outbreaks were reported, accounting for at least 431 cases of illness, 102 hospitalizations, and 14 deaths. Legionella was responsible for 66% of outbreaks and 26% of illnesses, and viruses and non-Legionella bacteria together accounted for 16% of outbreaks and 53% of illnesses. The two most commonly identified deficiencies† leading to drinking water-associated outbreaks were Legionella in building plumbing§ systems (66%) and untreated groundwater (13%). Continued vigilance by public health, regulatory, and industry professionals to identify and correct deficiencies associated with building plumbing systems and groundwater systems could prevent most reported outbreaks and illnesses associated with drinking water systems.
Figures
References
-
- Cutler D, Miller G. The role of public health improvements in health advances: the twentieth-century United States. Demography. 2005;42:1–22. - PubMed
-
-
National Primary Drinking Water Regulations: Ground Water Rule. 40 C.F.R. Sect. 141.400 (2006)
-
-
-
National Primary Drinking Water Regulations: Revisions to the Total Coliform Rule. 40 C.F.R. Sect. 141.851 (2013)
-
-
- Brunkard JM, Ailes E, Roberts VA, et al. Surveillance for waterborne disease outbreaks associated with drinking water—United States, 2007–2008. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2011;60(SS-12):38–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

