Rapid maxillary expansion in therapy-resistant enuretic children: An orthodontic perspective
- PMID: 26270462
- PMCID: PMC8601747
- DOI: 10.2319/051515-329.1
Rapid maxillary expansion in therapy-resistant enuretic children: An orthodontic perspective
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate whether rapid maxillary expansion (RME) could reduce the frequency of nocturnal enuresis (NE) in children and whether a placebo effect could be ruled out.
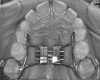
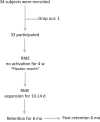
Methods: Thirty-four subjects, 29 boys and five girls with mean age of 10.7 ± 1.8 years suffering from primary NE, were recruited. All subjects were nonresponders to the first-line antienuretic treatment and therefore were classified as "therapy resistant." To rule out a placebo effect of the RME appliance, all children were first treated with a passive appliance for 4 weeks. Rhinomanometry (RM), acoustic rhinometry (AR), polysomnographic registration, and study casts were made at different time points.
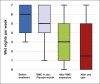
Results: One child experienced severe discomfort from the RME appliance and immediately withdrew from the study. Following RME, the long-term cure rate after 1 year was 60%. The RM and AR measurements at baseline and directly after RME showed a significant increase in nasal volume and nasal airflow, and there was a statistically significant correlation between reduction in enuresis and increase in nasal volume. Six months postretention, a 100% relapse of the dental overexpansion could be noted.
Conclusions: RME has a curative effect in some children with NE, which could be connected to the positive influence of RME on the sleep architecture. Normal transverse occlusion does not seem to be a contraindication for moderate maxillary expansion in attempts to cure NE in children.
Keywords: Nocturnal enuresis; Rapid maxillary expansion.
Figures
References
-
- Austin P, Bauer S, Bower W, et al. The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: update report from the standardization committee of the International Children’s Continence Society. J Urol. 2014;191:1863–1865. - PubMed
-
- Hjälmås K, Arnold T, Bower W, et al. Nocturnal enuresis: an international evidence based management strategy. J Urol. 2004;171:2545–2561. - PubMed
-
- Hirasing RA, van Leerdam FJ, Bolk-Bennink L, Janknegt RA. Enuresis nocturna in adults. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1997;31:533–536. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell PH, Deshpande AV, Von Gontard A. Management of nocturnal enuresis. BMJ. 2013;347:f6259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials