Serum eotaxin-1 is increased in extremely-low-birth-weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia or death
- PMID: 26270578
- PMCID: PMC4628573
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2015.152
Serum eotaxin-1 is increased in extremely-low-birth-weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia or death
Abstract
Background: Early systemic inflammation in extremely-low-birth-weight (ELBW) infants is associated with an increased risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). Our objective was to identify circulating biomarkers and develop prediction models for BPD/death soon after birth.
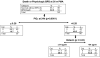
Methods: Blood samples from postnatal day 1 were analyzed for C-reactive protein (CRP) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and for 39 cytokines/chemokines by a multiplex assay in 152 ELBW infants. The primary outcome was physiologic BPD or death by 36 wk. CRP, cytokines, and clinical variables available at ≤24 h were used for forward stepwise regression and Classification and Regression Tree (CART) analysis to identify predictors of BPD/death.
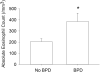
Results: Overall, 24% developed BPD and 35% died or developed BPD. Regression analysis identified birth weight and eotaxin (CCL11) as the two most significant variables. CART identified FiO2 at 24 h (11% BPD/death if FiO2 ≤28%, 49% if >28%) and eotaxin in infants with FiO2 > 28% (29% BPD/death if eotaxin was ≤84 pg/ml; 65% if >84) as variables most associated with outcome.
Conclusion: Eotaxin measured on the day of birth is useful for identifying ELBW infants at risk of BPD/death. Further investigation is required to determine if eotaxin is involved in lung injury and pathogenesis of BPD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196:147.e141–148. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari A, Bhandari V. Pitfalls, problems, and progress in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 2009;123:1562–1573. - PubMed
-
- Koksal N, Kayik B, Cetinkaya M, et al. Value of serum and bronchoalveolar fluid lavage pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels for predicting bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2012;23:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Munshi UK, Niu JO, Siddiq MM, Parton LA. Elevation of interleukin-8 and interleukin-6 precedes the influx of neutrophils in tracheal aspirates from preterm infants who develop bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1997;24:331–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

