Emerging and Underrecognized Complications of Illicit Drug Use
- PMID: 26270683
- PMCID: PMC4657534
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ689
Emerging and Underrecognized Complications of Illicit Drug Use
Abstract
Illicit drug use can result in a wide range of medical complications. As the availability, synthesis, and popularity of illicit drugs evolve over time, new syndromes associated with their use may mimic infections. Some of these symptoms are anticipated drug effects, and others are complications of adulterants mixed with drugs or complications from the method of using drugs. Some illicit drugs are associated with rare infections, which are difficult to diagnosis with standard microbiological techniques. The goal of this review is to orient a wide range of clinicians-including general practitioners, emergency medicine providers, and infectious diseases specialists-to complications of illicit drug use that may be underrecognized. Improving awareness of infectious and noninfectious complications of illicit drug can expedite diagnosis and medical treatment of persons who use drugs and facilitate targeted harm reduction counseling to prevent future complications.
Keywords: altered mental status; illicit drug use; injection drug use; skin and soft-tissue infections; substance abuse.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
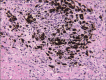

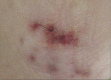

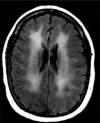
References
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: summary of national findings. NSDUH series H-48 2014; HHS publication (SMA) 14–4863 Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2014. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUHresultsPDFWHTML2013/.... Accessed 4 September 2015.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Injury prevention & control: prescription drug overdose: data overview. 2015. Available at: www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/data/overdose/html. Accessed 2 July 2015.
-
- Cicero TJ, Kuehn BM. Driven by prescription drug abuse, heroin use increases among suburban and rural whites. JAMA 2014; 312:118–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

