Silencing of tripartite motif (TRIM) 29 inhibits proliferation and invasion and increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in human lung squamous cancer NCI-H520 cells
- PMID: 26273332
- PMCID: PMC4448470
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12130
Silencing of tripartite motif (TRIM) 29 inhibits proliferation and invasion and increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in human lung squamous cancer NCI-H520 cells
Abstract
Background: TRIM29 belongs to the tripartite motif (TRIM) protein family. It has been reported to be a tumor suppressor or have oncogenic function in many cancer types. The aim of this study was to investigate whether downregulation of TRIM29 by small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) could inhibit cell proliferation and invasion and increase chemosensitivity to cisplatin in human lung squamous cancer NCI-H520 cells in vitro.
Methods: We transformed TRIM29 siRNA into NCI-H520 cells. Real time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting assay were employed to determine TRIM29 messenger (m)RNA and protein expressions. MTT assay was used to determine the cell proliferation. Transwell invasion assay was used to determine the cell invasion. An Annexin V-propidium iodide (AnnV/PI) staining apoptosis test was used for detecting apoptosis.
Results: TRIM29 siRNA could specifically and efficiently suppress TRIM29 expression at both mRNA and protein levels. Silencing of the TRIM29 by siRNA in NCI-H520 cells inhibited cell proliferation and invasion in vitro. TRIM29 knockdown resulted in chemosensitivity enhancement in NCI-H520 cells.
Conclusion: Downregulation of TRIM29 can lead to potent antitumor activity and chemosensitizing effect in human lung squamous cancer NCI-H520 cells.
Keywords: Chemosensitivity; TRIM29; lung cancer; siRNA.
Figures
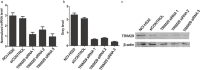

 , NCI-H520;
, NCI-H520;  , siCONTROL;
, siCONTROL;  , TRIM29 siRNA.
, TRIM29 siRNA.
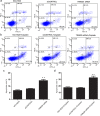
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010 CA Cancer J Clin 61. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. . (Published erratum appears in 2011;: 133–4) - PubMed
-
- Min XJ, Li H, Hou SC, et al. Dysfunction of volume-sensitive chloride channels contributes to cisplatin resistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2011;236:483–491. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

