Suppressive Effects of Plumbagin on Invasion and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells via the Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling and Down-regulation of Inflammatory Cytokine Expressions
- PMID: 26273514
- PMCID: PMC4472116
- DOI: 10.4248/BR201304007
Suppressive Effects of Plumbagin on Invasion and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells via the Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling and Down-regulation of Inflammatory Cytokine Expressions
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Suppressive effects of plumbagin on invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via the inhibition of STAT3 signaling and down-regulation of inflammatory cytokine expressions.Bone Res. 2019 May 22;7:16. doi: 10.1038/s41413-019-0052-0. eCollection 2019. Bone Res. 2019. PMID: 31123621 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of plumbagin (PL), a naphthoquinone derived from the medicinal plant plumbago zeylanica, on the invasion and migration of human breast cancer cells.
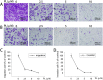
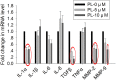
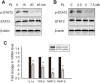
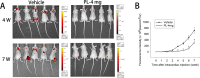
Methods: Human breast cancer MDA-MB-231SArfp cells were treated with different concentrations of plumbagin for 24 h. The effects of plumbagin on the migration and invasion were observed by a transwell method. The expressions of IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TGF-β, TNFα, MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA in MDA-MB-231SArfp cells were detected using Real-Time PCR. MDA-MB-231SArfp cells were treated with plumbagin at different concentrations for 45 minutes. The activation of STAT3 was detected by western blot. Following this analysis, STAT3 in MDA-MB-231SArfp cells was knocked out using specific siRNA. mRNA levels of IL-1α, TGF-β, MMP-2 and MMP-9 were then detected. Consequently, MDA-MB-231SArfp cells were injected intracardially into BALB/c nude mice to construct a breast cancer bone metastatic model. The mice were injected intraperitoneally with plumbagin. Non-invasive in vivo monitoring, X-ray imaging and histological staining were performed to investigate the effects of plumbagin on the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells in vivo.
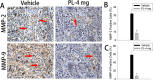
Results: The in vitro results showed that plumbagin could suppress the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells and down-regulate mRNA expressions of IL-1α, TGF-β, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Western blotting demonstrated that plumbagin inhibited the activation of STAT3 signaling in MDA-MB-231SArfp cells. The inactivation of STAT3 was found to have an inhibitory effect on the expressions of IL-1α, TGF-β, MMP-2 and MMP-9. In vivo studies showed that plumbagin inhibited the metastasis of breast cancer cells and decreased osteolytic bone metastases, as well as the secretion of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by tumor cells at metastatic lesions.
Conclusions: Plumbagin can suppress the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via the inhibition of STAT3 signaling and by downregulation of IL-1α, TGF-β, MMP-2 and MMP-9.
Keywords: breast cancer; invasion; migration; plumbagin.
Figures

References
-
- Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2137–2150. - PubMed
-
- Mundy GR. Metastasis to bone: causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:584–593. - PubMed
-
- Rose AA, Siegel PM. Breast cancer-derived factors facilitate osteolytic bone metastases. Bull Cancer. 2006;93:931–943. - PubMed
-
- Mundy GR. Mechanisms of bone metastases. Cancer. 1997;80:1546–1556. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

