CSF neurofilament light chain reflects corticospinal tract degeneration in ALS
- PMID: 26273687
- PMCID: PMC4531057
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.212
CSF neurofilament light chain reflects corticospinal tract degeneration in ALS
Abstract
Objective: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is sensitive to white matter tract pathology. A core signature involving the corticospinal tracts (CSTs) has been identified in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Raised neurofilament light chain protein (NfL) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is thought to reflect axonal damage in a range of neurological disorders. The relationship between these two measures was explored.
Methods: CSF and serum NfL concentrations and DTI acquired at 3 Tesla on the same day were obtained from ALS patients (n = 25 CSF, 40 serum) and healthy, age-similar controls (n = 17 CSF, 25 serum). Within-group correlations between NfL and DTI measures of microstructural integrity in major white matter tracts (CSTs, superior longitudinal fasciculi [SLF], and corpus callosum) were performed using tract-based spatial statistics.
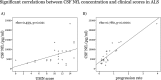
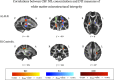
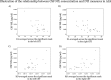
Results: NfL levels were higher in patients compared to controls. CSF levels correlated with clinical upper motor neuron burden and rate of disease progression. Higher NfL levels were significantly associated with lower DTI fractional anisotropy and increased radial diffusivity in the CSTs of ALS patients, but not in controls.
Interpretation: Elevated CSF and serum NfL is, in part, a result of CST degeneration in ALS. This highlights the wider potential for combining neurochemical and neuroimaging-based biomarkers in neurological disease.
Figures
References
-
- Bowser R, Turner MR, Shefner J. Biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: opportunities and limitations. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7:631–638. - PubMed
-
- Tortelli R, Ruggieri M, Cortese R, et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light levels in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a possible marker of disease severity and progression. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19:1561–1567. - PubMed
-
- Brettschneider J, Petzold A, Sussmuth SD, et al. Axonal damage markers in cerebrospinal fluid are increased in ALS. Neurology. 2006;66:852–856. - PubMed
-
- Rosengren LE, Karlsson JE, Karlsson JO, et al. Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases have increased levels of neurofilament protein in CSF. J Neurochem. 1996;67:2013–2018. - PubMed
-
- Tortelli R, Copetti M, Ruggieri M, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain levels: marker of progression to generalized amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2015;22:215–218. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- TURNER/JAN13/944-795/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- MALASPINA/APR13/817-791/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- G0701923/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MALASPINA/APR13/6097/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- MR/K01014X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

