Bio-Conjugated CNT-Bridged 3D Porous Graphene Oxide Membrane for Highly Efficient Disinfection of Pathogenic Bacteria and Removal of Toxic Metals from Water
- PMID: 26273843
- PMCID: PMC4690451
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b05012
Bio-Conjugated CNT-Bridged 3D Porous Graphene Oxide Membrane for Highly Efficient Disinfection of Pathogenic Bacteria and Removal of Toxic Metals from Water
Abstract
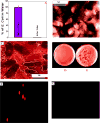
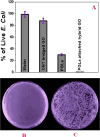
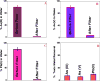
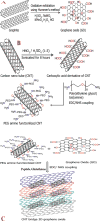
More than a billion people lack access to safe drinking water that is free from pathogenic bacteria and toxic metals. The World Health Organization estimates several million people, mostly children, die every year due to the lack of good quality water. Driven by this need, we report the development of PGLa antimicrobial peptide and glutathione conjugated carbon nanotube (CNT) bridged three-dimensional (3D) porous graphene oxide membrane, which can be used for highly efficient disinfection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacteria and removal of As(III), As(V), and Pb(II) from water. Reported results demonstrate that versatile membrane has the capability to capture and completely disinfect pathogenic pathogenic E. coli O157:H7 bacteria from water. Experimentally observed disinfection data indicate that the PGLa attached membrane can dramatically enhance the possibility of destroying pathogenic E. coli bacteria via synergistic mechanism. Reported results show that glutathione attached CNT-bridged 3D graphene oxide membrane can be used to remove As(III), As(V), and Pb(II) from water sample at 10 ppm level. Our data demonstrated that PGLa and glutathione attached membrane has the capability for high efficient removal of E. coli O157:H7 bacteria, As(III), As(V), and Pb(II) simultaneously from Mississippi River water.
Keywords: 3D porous graphene oxide membrane; As(V) and Pb(II) from water; CNT-bridged graphene oxide; E. coli O157:H7 bacteria removal; bacteria disinfection; separation of As(III).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Drinking Water Chlorination: A Review of Disinfection Practices and Issues. http://www.waterandhealth.org/drinkingwater/wp.html, date of access 03/12/2015.
-
- Billions affected daily by water and sanitation crisis. http://water.org/water-crisis/one-billion-affected/, date of access 03/12/2015.
-
- Health through safe drinking water and basic sanitation. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/mdg1/en/, date of access 03/12/2015.
-
- Health Topics: Arsenic. http://www.who.int/topics/arsenic/en/, date of access 03/12/2015.
-
- Pal S, Joardar J, Song J. Removal of E. coli from Water Using Surface-Modified Activated Carbon Filter Media and Its Performance over an Extended Use. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40:6091–6097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

