Differential Association of Psychosocial Comorbidities With Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 26274015
- PMCID: PMC6058701
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.22635
Differential Association of Psychosocial Comorbidities With Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events and subclinical atherosclerosis, but the reasons for the excess risk are unclear. We explored whether psychosocial comorbidities, which may be associated with CVD in the general population, are differentially associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in RA compared to controls.
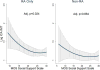
Methods: Data were from a longitudinal cohort study of 195 RA patients and 1,073 non-RA controls. Using validated scales, heterogeneity in the associations of psychosocial measures (depression, stress, anxiety/anger, support, discrimination/hassles) with measures of subclinical atherosclerosis (coronary artery calcium [CAC] and carotid intima-media thickness [IMT]/plaque) were compared in RA and non-RA groups using multivariable generalized linear models. Computed tomography and ultrasound were used to identify CAC and IMT/plaque, respectively. CAC >100 units was used to define moderate/severe CAC.
Results: In RA, per-unit higher anxiety scores (odds ratio [OR] 1.10, P = 0.029), anger scores (OR 1.14, P = 0.037), depressive symptoms (OR 3.41, P = 0.032), and caregiver stress (OR 2.86, P = 0.014) were associated with increased odds of CAC >100 units after adjustment for relevant covariates. These findings persisted despite adjustment for markers of inflammation (C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels) and were seen only in RA, not in controls (adjusted multiplicative interaction P = 0.001-0.077). In RA, job stress was associated with an increased risk of carotid plaque (adjusted OR = 3.21, P = 0.019), and increasing social support was associated with lower internal carotid IMT (adjusted P = 0.024).
Conclusion: Depressive symptoms, stress, anger/anxiety, and social support may preferentially affect CVD risk in RA, and screening/treatment for psychosocial morbidities in RA may help ameliorate the additional CVD burden.
© 2015, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Hollan I, Meroni PL, Ahearn JM, Cohen Tervaert JW, Curran S, Goodyear CS, et al. Cardiovascular disease in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:1004–15. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Mitchell DM, Sibley JT, Fries JF, Bloch DA, Williams CA, et al. The mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:481–94. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Llorca J, Martin J, Gonzalez-Gay MA. Carotid intima-media thickness predicts the development of cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2009;38:366–71. - PubMed
-
- Ku IA, Imboden JB, Hsue PY, Ganz P. Rheumatoid arthritis: model of systemic inflammation driving atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2009;73:977–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

