Spatial and Temporal Control of Cavitation Allows High In Vitro Transfection Efficiency in the Absence of Transfection Reagents or Contrast Agents
- PMID: 26274324
- PMCID: PMC4537239
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134247
Spatial and Temporal Control of Cavitation Allows High In Vitro Transfection Efficiency in the Absence of Transfection Reagents or Contrast Agents
Abstract
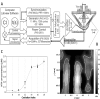
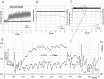
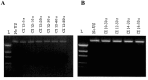
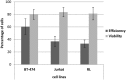
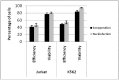
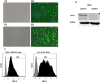
Sonoporation using low-frequency high-pressure ultrasound (US) is a non-viral approach for in vitro and in vivo gene delivery. In this study, we developed a new sonoporation device designed for spatial and temporal control of ultrasound cavitation. The regulation system incorporated in the device allowed a real-time control of the cavitation level during sonoporation. This device was evaluated for the in vitro transfection efficiency of a plasmid coding for Green Fluorescent Protein (pEGFP-C1) in adherent and non-adherent cell lines. The transfection efficiency of the device was compared to those observed with lipofection and nucleofection methods. In both adherent and non-adherent cell lines, the sonoporation device allowed high rate of transfection of pEGFP-C1 (40-80%), as determined by flow cytometry analysis of GFP expression, along with a low rate of mortality assessed by propidium iodide staining. The transfection efficiency and toxicity of sonoporation on the non-adherent cell lines Jurkat and K562 were similar to those of nucleofection, while these two cell lines were resistant to transfection by lipofection. Moreover, sonoporation was used to produce three stably transfected human lymphoma and leukemia lines. Significant transfection efficiency was also observed in two fresh samples of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. In conclusion, we developed a user-friendly and cost-effective ultrasound device, well adapted for routine in vitro high-yield transfection experiments and which does not require the use of any transfection reagent or gas micro-bubbles.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Marshall E (1999) Gene therapy death prompts review of adenovirus vector. Science 286: 2244–2245. - PubMed
-
- Baum C, Kustikova O, Modlich U, Li Z, fehse B (2006) Mutagenesis and oncogenesis by chromosomal insertion of gene transfer vectors. Hum Gene Ther 17: 253–263. - PubMed
-
- Pack DW, Hoffman AS, Pun S, Stayton PS (2005) Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5: 581–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

