Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for Clinical Diagnosis of 561 Mendelian Diseases
- PMID: 26274329
- PMCID: PMC4537117
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133636
Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for Clinical Diagnosis of 561 Mendelian Diseases
Erratum in
-
Correction: Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for Clinical Diagnosis of 561 Mendelian Diseases.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 22;10(9):e0139258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139258. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26393808 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correction: Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for Clinical Diagnosis of 561 Mendelian Diseases.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 28;11(1):e0148154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148154. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26820312 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a cost-effective approach for rapid and accurate detection of genetic mutations in patients with suspected genetic disorders, which can facilitate effective diagnosis.
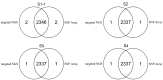
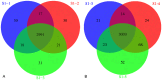
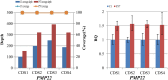
Methodology/principal findings: We designed a capture array to mainly capture all the coding sequence (CDS) of 2,181 genes associated with 561 Mendelian diseases and conducted NGS to detect mutations. The accuracy of NGS was 99.95%, which was obtained by comparing the genotypes of selected loci between our method and SNP Array in four samples from normal human adults. We also tested the stability of the method using a sample from normal human adults. The results showed that an average of 97.79% and 96.72% of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) in the sample could be detected stably in a batch and different batches respectively. In addition, the method could detect various types of mutations. Some disease-causing mutations were detected in 69 clinical cases, including 62 SNVs, 14 insertions and deletions (Indels), 1 copy number variant (CNV), 1 microdeletion and 2 microduplications of chromosomes, of which 35 mutations were novel. Mutations were confirmed by Sanger sequencing or real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Conclusions/significance: Results of the evaluation showed that targeted NGS enabled to detect disease-causing mutations with high accuracy, stability, speed and throughput. Thus, the technology can be used for the clinical diagnosis of 561 Mendelian diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Validation of Copy Number Variant Detection from Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Panels.J Mol Diagn. 2017 Nov;19(6):905-920. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Aug 15. J Mol Diagn. 2017. PMID: 28818680
-
Next-generation sequencing using a pre-designed gene panel for the molecular diagnosis of congenital disorders in pediatric patients.Hum Genomics. 2015 Dec 14;9:33. doi: 10.1186/s40246-015-0055-x. Hum Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26666243 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of sequence variants in genetic disease-causing genes using targeted next-generation sequencing.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029500. Epub 2011 Dec 21. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22216297 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Applications of Next-Generation Sequencing in Cancer Diagnosis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2017 Apr;23(2):225-234. doi: 10.1007/s12253-016-0124-z. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Pathol Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 27722982 Review.
-
Detection of structural DNA variation from next generation sequencing data: a review of informatic approaches.Cancer Genet. 2013 Dec;206(12):432-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Cancer Genet. 2013. PMID: 24405614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of targeted panel sequencing and whole exome sequencing for 76 Chinese families with retinitis pigmentosa.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Mar;8(3):e1131. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1131. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 31960602 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-Exome Target Sequencing in a Family With Syndactyly Type IV Due to a Novel Partial Duplication of the LMBR1 Gene: First Case Report in Fujian Province of China.Front Genet. 2020 Feb 28;11:130. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00130. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32184803 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Sequencing and RNA Assay Reveal a Noncanonical JAG1 Splicing Variant Causing Alagille Syndrome.Front Genet. 2020 Jan 24;10:1363. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01363. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32038717 Free PMC article.
-
The c.1243T>C mutation in the PROC gene is linked with inherited protein C deficiency and severe purpura fulminans.Clin Case Rep. 2023 Dec 1;11(12):e8280. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.8280. eCollection 2023 Dec. Clin Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 38046799 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and challenges of 5G network technology toward precision medicine.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Nov;16(11):2078-2094. doi: 10.1111/cts.13640. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37702288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brinkman RR, Dube MP, Rouleau GA, Orr AC, Samuels ME. Human monogenic disorders—a source of novel drug targets. Nature reviews Genetics. 2006; 7(4): 249–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

