Clinical Electroencephalography for Anesthesiologists: Part I: Background and Basic Signatures
- PMID: 26275092
- PMCID: PMC4573341
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000841
Clinical Electroencephalography for Anesthesiologists: Part I: Background and Basic Signatures
Abstract
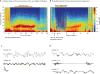
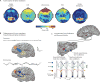
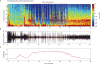
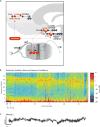
The widely used electroencephalogram-based indices for depth-of-anesthesia monitoring assume that the same index value defines the same level of unconsciousness for all anesthetics. In contrast, we show that different anesthetics act at different molecular targets and neural circuits to produce distinct brain states that are readily visible in the electroencephalogram. We present a two-part review to educate anesthesiologists on use of the unprocessed electroencephalogram and its spectrogram to track the brain states of patients receiving anesthesia care. Here in part I, we review the biophysics of the electroencephalogram and the neurophysiology of the electroencephalogram signatures of three intravenous anesthetics: propofol, dexmedetomidine, and ketamine, and four inhaled anesthetics: sevoflurane, isoflurane, desflurane, and nitrous oxide. Later in part II, we discuss patient management using these electroencephalogram signatures. Use of these electroencephalogram signatures suggests a neurophysiologically based paradigm for brain state monitoring of patients receiving anesthesia care.
Conflict of interest statement
Masimo has signed an agreement with Massachusetts General Hospital to license the signal processing algorithms developed by Drs. Brown and Purdon for analysis of the electroencephalogram to track the brain states of patients receiving general anesthesia and sedation for incorporation into their brain function monitors.
Figures


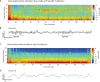

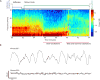

References
-
- Gibbs FA, Gibbs LE, Lennox WG. Effects on the electroencephalogram of certain drugs which influence nervous activity. Arch Intern Med. 1937;60:154–66.
-
- Faulconer A, Bickford RG. Electroencephalography in anesthesiology. Springfield, Ill.: Thomas; 1960. - PubMed
-
- Faulconer A, Pender JW, Bickford RG. The influence of partial pressure of nitrous oxide on the depth of anesthesia and the electro-encephalogram in man. Anesthesiology. 1949;10:601–9. - PubMed
-
- Kiersey DK, Bickford RG, Faulconer A., Jr Electro-encephalographic patterns produced by thiopental sodium during surgical operations; description and classification. Br J Anaesth. 1951;23:141–52. - PubMed
-
- Galla SJ, Rocco AG, Vandam LD. Evaluation of the traditional signs and stages of anesthesia: an electroencephalographic and clinical study. Anesthesiology. 1958;19:328–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

