Steatosis and hepatitis C
- PMID: 26276502
- PMCID: PMC4760068
- DOI: 10.1093/gastro/gov040
Steatosis and hepatitis C
Abstract
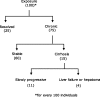
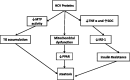
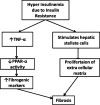
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a common liver disease worldwide with a high rate of chronicity (75-80%) in infected individuals. The chronic form of HCV leads to steatosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellualr carcinoma. Steatosis is prevalent in HCV patients (55%) due to a combination of viral factors (effect of viral proteins on some of the intracellular pathways) and host factors (overweight, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, and alcohol consumption). The response rates to treatment of chronic HCV with pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN) and (in the case of genotype-1 HCV, the most common infecting genotype in the USA) ribavirin (RBV) is low, with a sustained viral response rate ≤ 40%. Adding direct-acting antiviral agents-recently approved by the FDA-to the standard protocol has increased the response rate; however HCV-related end-stage liver disease is still the primary indication for liver transplantation in the USA. The focus of this article is on the interrelation between HCV, steatosis and metabolic syndrome.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press and the Digestive Science Publishing Co. Limited.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sustained virological response to pegylated interferon plus ribavirin leads to normalization of liver stiffness in hepatitis C virus-infected patients.Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013 Aug-Sep;31(7):424-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2012.12.004. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013. PMID: 23453582
-
Alisporivir plus ribavirin, interferon free or in combination with pegylated interferon, for hepatitis C virus genotype 2 or 3 infection.Hepatology. 2015 Oct;62(4):1013-23. doi: 10.1002/hep.27960. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 26118427 Clinical Trial.
-
Boceprevir plus pegylated interferon/ribavirin to re-treat hepatitis C virus genotype 1 in HIV-HCV co-infected patients: final results of the Spanish BOC HIV-HCV Study.Int J Infect Dis. 2016 Dec;53:46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2016.10.028. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Int J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27815225 Clinical Trial.
-
A pharmacological profile of ribavirin and monitoring of its plasma concentration in chronic hepatitis C infection.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2012 Mar;2(1):42-54. doi: 10.1016/S0973-6883(12)60090-5. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 25755405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond interferon: rationale and prospects for newer treatment paradigms for chronic hepatitis C.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2015 Jan;6(1):4-14. doi: 10.1177/2040622314551934. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2015. PMID: 25553238 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiological, Molecular and Therapeutic Issues of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 20;20(8):1948. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081948. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31010049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus-Lipid Interplay: Pathogenesis and Clinical Impact.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 19;11(2):271. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020271. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Megamitochondria formation in hepatocytes of patient with chronic hepatitis C - a case report.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017 Sep;3(3):169-175. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2017.68287. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 29062908 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus core protein: Not just a nucleocapsid building block, but an immunity and inflammation modulator.Tzu Chi Med J. 2021 Sep 24;34(2):139-147. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_97_21. eCollection 2022 Apr-Jun. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021. PMID: 35465281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Hepatic Steatosis Before and After Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment in People With HIV and Hepatitis C Coinfection.J Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 4;231(1):e101-e112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae487. J Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39417816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rustgi VK. The epidemiology of hepatitis C infection in the United States. J Gastroenterol 2007;42:513–21. - PubMed
-
- Qureshi SA, Qureshi H, Hameed A. Hepatitis C therapy—the future looks bright. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2009 Dec;28:1409–13. - PubMed
-
- Marcellin P, Asselah T, Boyer N. Fibrosis and disease progression in hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002;36:S47–56. - PubMed
-
- Hourigan LF, Macdonald GA, Purdie D, et al. Fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C correlates significantly with body mass index and steatosis. Hepatology 1999;29:1215–19. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

