Automatic estimation and correction of anisotropic magnification distortion in electron microscopes
- PMID: 26278979
- PMCID: PMC6760661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.08.006
Automatic estimation and correction of anisotropic magnification distortion in electron microscopes
Abstract
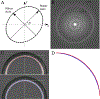
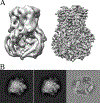
We demonstrate a significant anisotropic magnification distortion, found on an FEI Titan Krios microscope and affecting magnifications commonly used for data acquisition on a Gatan K2 Summit detector. We describe a program (mag_distortion_estimate) to automatically estimate anisotropic magnification distortion from a set of images of a standard gold shadowed diffraction grating. We also describe a program (mag_distortion_correct) to correct for the estimated distortion in collected images. We demonstrate that the distortion present on the Titan Krios microscope limits the resolution of a set of rotavirus VP6 images to ∼7 Å, which increases to ∼3 Å following estimation and correction of the distortion. We also use a 70S ribosome sample to demonstrate that in addition to affecting resolution, magnification distortion can also interfere with the classification of heterogeneous data.
Keywords: Electron cryo-microscopy; Image correction; Magnification anisotropy; Resolution.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

