Species Delimitation in the Genus Moschus (Ruminantia: Moschidae) and Its High-Plateau Origin
- PMID: 26280166
- PMCID: PMC4539215
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134183
Species Delimitation in the Genus Moschus (Ruminantia: Moschidae) and Its High-Plateau Origin
Abstract
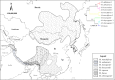
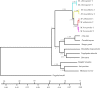
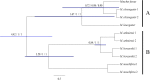
The authenticity of controversial species is a significant challenge for systematic biologists. Moschidae is a small family of musk deer in the Artiodactyla, composing only one genus, Moschus. Historically, the number of species in the Moschidae family has been debated. Presently, most musk deer species were restricted in the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding/adjacent areas, which implied that the evolution of Moschus might have been punctuated by the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. In this study, we aimed to determine the evolutionary history and delimit the species in Moschus by exploring the complete mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) and other mitochondrial gene. Our study demonstrated that six species, M. leucogaster, M. fuscus, M. moschiferus, M. berezovskii, M. chrysogaster and M. anhuiensis, were authentic species in the genus Moschus. Phylogenetic analysis and molecular dating showed that the ancestor of the present Moschidae originates from Tibetan Plateau which suggested that the evolution of Moschus was prompted by the most intense orogenic movement of the Tibetan Plateau during the Pliocene age, and alternating glacial-interglacial geological eras.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial genome of captive Alpine musk deer, Moschus chrysogaster (Moschidae), and phylogenetic analyses with its coordinal species.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Feb 13;6(2):598-600. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1875930. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021. PMID: 33628944 Free PMC article.
-
The complete mitochondrial genome of the Alpine musk deer (Moschus chrysogaster).Mitochondrial DNA. 2013 Oct;24(5):501-3. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2013.770504. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Mitochondrial DNA. 2013. PMID: 23577614
-
Mitochondrial genome of the Alpine musk deer Moschus chrysogaster (Artiodactyla: Ruminantia: Moschidae).Mitochondrial DNA. 2013 Oct;24(5):487-9. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2013.770499. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Mitochondrial DNA. 2013. PMID: 23560692
-
Phylogenetic study of complete cytochrome b genes in musk deer (genus Moschus) using museum samples.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1999 Aug;12(3):241-9. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1999.0616. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1999. PMID: 10413620
-
The Ruminant Telomere-to-Telomere (RT2T) Consortium.Nat Genet. 2024 Aug;56(8):1566-1573. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01835-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 39103649 Review.
Cited by
-
A brighter shade of future climate on Himalayan musk deer Moschus leucogaster.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 7;13(1):12771. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39481-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37550330 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial genome of captive Alpine musk deer, Moschus chrysogaster (Moschidae), and phylogenetic analyses with its coordinal species.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Feb 13;6(2):598-600. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1875930. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021. PMID: 33628944 Free PMC article.
-
Systematics of the Artiodactyla of China in the 21(st) century.Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2016 May 18;37(3):119-25. doi: 10.13918/j.issn.2095-8137.2016.3.119. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2016. PMID: 27265649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple independent structural dynamic events in the evolution of snake mitochondrial genomes.BMC Genomics. 2018 May 10;19(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4717-7. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29747572 Free PMC article.
-
Empirical Data Suggest That the Kashmir Musk Deer (Moschus cupreus, Grubb 1982) Is the One Musk Deer Distributed in the Western Himalayas: An Integration of Ecology, Genetics and Geospatial Modelling Approaches.Biology (Basel). 2023 May 29;12(6):786. doi: 10.3390/biology12060786. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Willis KJ, Whittaker RJ (2002) Species diversity–scale matters. Science 295: 1245–1248. - PubMed
-
- Pearson RG, Dawson TP (2003) Predicting the impacts of climate change on the distribution of species: are bioclimate envelope models useful? Global Ecol Biogeogr 12: 361–371.
-
- Chung SL, Lo CH, Lee TY, Zhang YQ, Xie YW, Li XH, et al. (1998) Diachronous uplift of the Tibetan plateau starting 40 Myr ago. Nature 394: 769–773.
-
- Zhang PZ, Shen ZK, Wang M, Gan WJ, Bürgmann R, Molnar P, et al. (2004) Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data. Geology 32: 809–812.
-
- Zhang DF, Fengquan L, Jianmin B (2000) Eco-environmental effects of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau uplift during the Quaternary in China. Environ Geol 39: 1352–1358.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

