Higher Matrix Stiffness Upregulates Osteopontin Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Mediated by Integrin β1/GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 26280346
- PMCID: PMC4539226
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134243
Higher Matrix Stiffness Upregulates Osteopontin Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Mediated by Integrin β1/GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
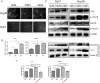
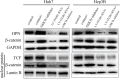
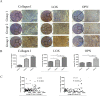
Increased stromal stiffness is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development and progression. However, the molecular mechanism by which matrix stiffness stimuli modulate HCC progress is largely unknown. In this study, we explored whether matrix stiffness-mediated effects on osteopontin (OPN) expression occur in HCC cells. We used a previously reported in vitro culture system with tunable matrix stiffness and found that OPN expression was remarkably upregulated in HCC cells with increasing matrix stiffness. Furthermore, the phosphorylation level of GSK3β and the expression of nuclear β-catenin were also elevated, indicating that GSK3β/β-catenin pathway might be involved in OPN regulation. Knock-down analysis of integrin β1 showed that OPN expression and p-GSK3β level were downregulated in HCC cells grown on high stiffness substrate compared with controls. Simultaneously, inhibition of GSK-3β led to accumulation of β-catenin in the cytoplasm and its enhanced nuclear translocation, further triggered the rescue of OPN expression, suggesting that the integrin β1/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway is specifically activated for matrix stiffness-mediated OPN upregulation in HCC cells. Tissue microarray analysis confirmed that OPN expression was positively correlated with the expression of LOX and COL1. Taken together, high matrix stiffness upregulated OPN expression in HCC cells via the integrin β1/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. It highlights a new insight into a pathway involving physical mechanical signal and biochemical signal molecules which contributes to OPN expression in HCC cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increasing matrix stiffness upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells mediated by integrin β1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Feb 14;444(3):427-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.079. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24472554
-
NDRG1 promotes growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by directly interacting with GSK-3β and Nur77 to prevent β-catenin degradation.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):29847-59. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4913. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26359353 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate stiffness promotes latent TGF-β1 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Jan 29;483(1):553-558. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.12.107. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28025149
-
Aberrant regulation of Wnt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep 7;22(33):7486-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7486. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27672271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pivotal roles of glycogen synthase-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 Aug;65:59-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 28619606 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanical homeostasis imbalance in hepatic stellate cells activation and hepatic fibrosis.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Apr 20;10:1183808. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1183808. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37152902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechano-Signaling Aspects of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2021 Sep 3;12(21):6411-6421. doi: 10.7150/jca.60102. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34659531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix stiffness-upregulated LOXL2 promotes fibronectin production, MMP9 and CXCL12 expression and BMDCs recruitment to assist pre-metastatic niche formation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 May 4;37(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0761-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29728125 Free PMC article.
-
Increased matrix stiffness promotes tumor progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient heat treatment.Cancer Sci. 2017 Sep;108(9):1778-1786. doi: 10.1111/cas.13322. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28699238 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Matrix Stiffness: New Areas Affecting Cell Metabolism.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 24;11:631991. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.631991. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718214 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El-Tanani MK: Role of osteopontin in cellular signaling and metastatic phenotype. Front Biosci 2008, 13:4276–4284. - PubMed
-
- Weber GF: The metastasis gene osteopontin: a candidate target for cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001, 1552:61–85. - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro SA, Oliveira JP: Osteopontin expression according to molecular profile of invasive breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers 2008, 23(3):154–60. - PubMed
-
- Visintin I, Feng Z, Longton G, Ward DC, Alvero AB, Lai Y, et al. Diagnostic markers for early detection of ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008, 15;14(4):1065–72. - PubMed
-
- Cho H, Hong SW, Oh YJ, Kim MA, Kang ES, Lee JM, et al. Clinical significance of osteopontin expression in cervical cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2008;134(8):909–17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

