Distinct regulatory mechanisms governing embryonic versus adult adipocyte maturation
- PMID: 26280538
- PMCID: PMC4553131
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3217
Distinct regulatory mechanisms governing embryonic versus adult adipocyte maturation
Abstract
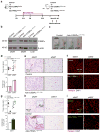
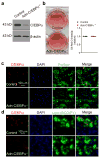
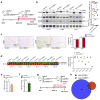
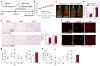
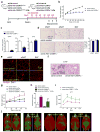
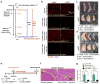
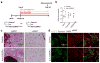
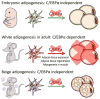
Pathological expansion of adipose tissue contributes to the metabolic syndrome. Distinct depots develop at various times under different physiological conditions. The transcriptional cascade mediating adipogenesis is established in vitro, and centres around a core program involving PPARγ and C/EBPα. We developed an inducible, adipocyte-specific knockout system to probe the requirement of key adipogenic transcription factors at various stages of adipogenesis in vivo. C/EBPα is essential for all white adipogenic conditions in the adult stage, such as adipose tissue regeneration, adipogenesis in muscle and unhealthy expansion of white adipose tissue during high-fat feeding or due to leptin deficiency. Surprisingly, terminal embryonic adipogenesis is fully C/EBPα independent, but does however depend on PPARγ; cold-induced beige adipogenesis is also C/EBPα independent. Moreover, C/EBPα is not vital for adipocyte survival in the adult stage. We reveal a surprising diversity of transcriptional signals required at different stages of adipogenesis in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pdcd4 restrains the self-renewal and white-to-beige transdifferentiation of adipose-derived stem cells.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Mar 31;7(3):e2169. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.75. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27031966 Free PMC article.
-
Role of C/EBPβ-LAP and C/EBPβ-LIP in early adipogenic differentiation of human white adipose-derived progenitors and at later stages in immature adipocytes.Differentiation. 2013 Jan;85(1-2):20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2012.11.001. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Differentiation. 2013. PMID: 23314288
-
Alpinia officinarum inhibits adipocyte differentiation and high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice through regulation of adipogenesis and lipogenesis.J Med Food. 2012 Nov;15(11):959-67. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2286. J Med Food. 2012. PMID: 23126661
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Adipogenesis.Compr Physiol. 2017 Mar 16;7(2):635-674. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c160022. Compr Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28333384 Review.
-
Molecular Regulation of Adipogenesis and Potential Anti-Adipogenic Bioactive Molecules.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 19;17(1):124. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010124. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26797605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity caused by an OVOL2 mutation reveals dual roles of OVOL2 in promoting thermogenesis and limiting white adipogenesis.Cell Metab. 2022 Nov 1;34(11):1860-1874.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.018. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Cell Metab. 2022. PMID: 36228616 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Adipocyte Precursors in Development and Obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 19;11:613606. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.613606. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33679601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Protein Restriction Modulates Lipid Metabolism in White Adipose Tissues and Alters Colonic Microbiota of Shaziling Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;12(21):2944. doi: 10.3390/ani12212944. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359067 Free PMC article.
-
Inside out: Bone marrow adipose tissue as a source of circulating adiponectin.Adipocyte. 2016 Mar 22;5(3):251-69. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2016.1149269. eCollection 2016 Jul-Sep. Adipocyte. 2016. PMID: 27617171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional networks controlling stromal cell differentiation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Jul;22(7):465-482. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00357-7. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33837369 Review.
References
-
- Scherer PE. Adipose tissue: from lipid storage compartment to endocrine organ. Diabetes. 2006;55:1537–1545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

