Knocking down disease: a progress report on siRNA therapeutics
- PMID: 26281785
- PMCID: PMC4756474
- DOI: 10.1038/nrg3978
Knocking down disease: a progress report on siRNA therapeutics
Abstract
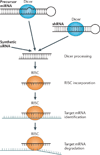
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which downregulate gene expression guided by sequence complementarity, can be used therapeutically to block the synthesis of disease-causing proteins. The main obstacle to siRNA drugs - their delivery into the target cell cytosol - has been overcome to allow suppression of liver gene expression. Here, we review the results of recent clinical trials of siRNA therapeutics, which show efficient and durable gene knockdown in the liver, with signs of promising clinical outcomes and little toxicity. We also discuss the barriers to more widespread applications that target tissues besides the liver and the most promising avenues to overcome them.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare
Figures
References
-
-
Stephenson ML, Zamecnik PC. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1978;75:285–288. First demonstration of the possibility of inhibiting gene expression using oligonucleotides.
-
-
- Bennett CF, Swayze EE. RNA targeting therapeutics: molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010;50:259–293. - PubMed
-
- Sharma VK, Sharma RK, Singh SK. Antisense oligonucleotides: modifications and clinical trials. Med. Chem. Commun. 2014;5:1454–1471.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

