Exome analysis of a family with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome identifies a novel disease locus
- PMID: 26284702
- PMCID: PMC4896306
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37297
Exome analysis of a family with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome identifies a novel disease locus
Abstract
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is a common cause of supraventricular tachycardia that carries a risk of sudden cardiac death. To date, mutations in only one gene, PRKAG2, which encodes the 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit γ-2, have been identified as causative for WPW. DNA samples from five members of a family with WPW were analyzed by exome sequencing. We applied recently designed prioritization strategies (VAAST/pedigree VAAST) coupled with an ontology-based algorithm (Phevor) that reduced the number of potentially damaging variants to 10: a variant in KCNE2 previously associated with Long QT syndrome was also identified. Of these 11 variants, only MYH6 p.E1885K segregated with the WPW phenotype in all affected individuals and was absent in 10 unaffected family members. This variant was predicted to be damaging by in silico methods and is not present in the 1,000 genome and NHLBI exome sequencing project databases. Screening of a replication cohort of 47 unrelated WPW patients did not identify other likely causative variants in PRKAG2 or MYH6. MYH6 variants have been identified in patients with atrial septal defects, cardiomyopathies, and sick sinus syndrome. Our data highlight the pleiotropic nature of phenotypes associated with defects in this gene.
Keywords: MYH6; Wolff-Parkinson-White; whole exome sequencing.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interests: none.
Figures


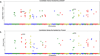
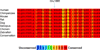
References
-
- Abbott GW, Sesti F, Splawski I, Buck ME, Lehmann MH, Timothy KW, Keating MT, Goldstein SA. MiRP1 forms IKr potassium channels with HERG and is associated with cardiac arrhythmia. Cell. 1999;97:175–187. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal P, Gill-Randall R, Wheatley T, Buchalter MB, Metcalfe J, Alcolado JC. Identification of mtDNA mutation in a pedigree with gestational diabetes, deafness, Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome and placenta accreta. Hum Hered. 2001;51:114–116. - PubMed
-
- Arrington CB, Sower CT, Chuckwuk N, Stevens J, Leppert MF, Yetman AT, Bowles NE. Absence of TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 mutations in patients with bicuspid aortic valve and aortic dilation. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102:629–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

