Genome-wide association of polycystic ovary syndrome implicates alterations in gonadotropin secretion in European ancestry populations
- PMID: 26284813
- PMCID: PMC4557132
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8502
Genome-wide association of polycystic ovary syndrome implicates alterations in gonadotropin secretion in European ancestry populations
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Genome-wide association of polycystic ovary syndrome implicates alterations in gonadotropin secretion in European ancestry populations.Nat Commun. 2016 Feb 12;7:10762. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10762. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26867975 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Publisher Correction: Genome-wide association of polycystic ovary syndrome implicates alterations in gonadotropin secretion in European ancestry populations.Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 28;11(1):2158. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15793-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32345980 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common, highly heritable complex disorder of unknown aetiology characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation and defects in glucose homeostasis. Increased luteinizing hormone relative to follicle-stimulating hormone secretion, insulin resistance and developmental exposure to androgens are hypothesized to play a causal role in PCOS. Here we map common genetic susceptibility loci in European ancestry women for the National Institutes of Health PCOS phenotype, which confers the highest risk for metabolic morbidities, as well as reproductive hormone levels. Three loci reach genome-wide significance in the case-control meta-analysis, two novel loci mapping to chr 8p23.1 [Corrected] and chr 11p14.1, and a chr 9q22.32 locus previously found in Chinese PCOS. The same chr 11p14.1 SNP, rs11031006, in the region of the follicle-stimulating hormone B polypeptide (FSHB) gene strongly associates with PCOS diagnosis and luteinizing hormone levels. These findings implicate neuroendocrine changes in disease pathogenesis.
Figures
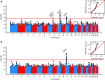
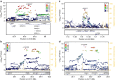


References
-
- Franks S., Stark J. & Hardy K. Follicle dynamics and anovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum. Reprod. Update 14, 367–378 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Eagleson C. A. et al.. Polycystic ovarian syndrome: evidence that flutamide restores sensitivity of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator to inhibition by estradiol and progesterone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 4047–4052 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Abbott D. H., Dumesic D. A. & Franks S. Developmental origin of polycystic ovary syndrome - a hypothesis. J. Endocrinol. 174, 1–5 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 DK65598/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD055936/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071895/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD01346/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD055942/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD056510/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK20595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 098381/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U10 HD039005/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27049/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD29364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD055925/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD034449/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057450/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033184/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK065598/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD029364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD057796/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD38998/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD038998/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057223/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD028934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD055944/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD39005/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD038992/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD28934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD38992/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- G9710020/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HD065029/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 086596/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U10 HD027049/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD001346/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR000127/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G0802782/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M012638/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD34449/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

