Overactivation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2-antioxidant response element pathway in hepatocytes decreases hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice
- PMID: 26285140
- PMCID: PMC4718744
- DOI: 10.1002/lt.24303
Overactivation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2-antioxidant response element pathway in hepatocytes decreases hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice
Abstract
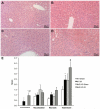
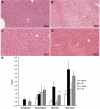
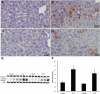
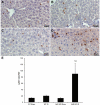
Hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) is a critical component of hepatic surgery. Oxidative stress has long been implicated as a key player in IRI. In this study, we examine the cell-specific role of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2)-antioxidant response element pathway in warm hepatic IRI. Nrf2 knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) animals and novel transgenic mice expressing a constitutively active nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (caNrf2) mutant in hepatocytes (AlbCre+/caNrf2+) and their littermate controls underwent partial hepatic ischemia or sham surgery. The animals were killed 6 hours after reperfusion, and their serum and tissue were collected for analysis. As compared to WT animals after ischemia/reperfusion (IR), Nrf2 KO mice had increased hepatocellular injury with increased serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, Suzuki score, apoptosis, an increased inflammatory infiltrate, and enhanced inflammatory cytokine expression. On the other hand, AlbCre+/caNrf2+ that underwent IR had significantly reduced serum transaminases, less necrosis on histology, and a less pronounced inflammatory infiltrate and inflammatory cytokine expression as compared to the littermate controls. However, there were no differences in apoptosis. Taken together, Nrf2 plays a critical role in our murine model of warm hepatic IRI, with Nrf2 deficiency exacerbating hepatic IRI and hepatocyte-specific Nrf2 overactivation providing protection against warm hepatic IRI.
© 2015 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cell-specific overactivation of nuclear erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2-mediated gene expression in myeloid cells decreases hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury.Liver Transpl. 2016 Aug;22(8):1115-28. doi: 10.1002/lt.24473. Liver Transpl. 2016. PMID: 27113842 Free PMC article.
-
KEAP1-NRF2 complex in ischemia-induced hepatocellular damage of mouse liver transplants.J Hepatol. 2013 Dec;59(6):1200-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Jul 16. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23867319 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 regulates toll-like receptor 4 innate responses in mouse liver ischemia-reperfusion injury through Akt-forkhead box protein O1 signaling network.Transplantation. 2014 Oct 15;98(7):721-8. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000316. Transplantation. 2014. PMID: 25171655 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+ T Cell NRF2 Signaling Improves Liver Transplantation Outcomes by Modulating T Cell Activation and Differentiation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Mar;38(7-9):670-683. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0094. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36070449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive overview of Nrf2-related epigenetic regulations involved in ischemia-reperfusion injury.Theranostics. 2022 Sep 11;12(15):6626-6645. doi: 10.7150/thno.77243. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36185600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Albumin promoter-driven FlpO expression induces efficient genetic recombination in mouse liver.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 May 1;326(5):G495-G503. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00263.2023. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38469630 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between oxidative stress and nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 signaling in diabetic cardiomyopathy (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):678. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10110. Epub 2021 Apr 25. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33986843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-specific overactivation of nuclear erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2-mediated gene expression in myeloid cells decreases hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury.Liver Transpl. 2016 Aug;22(8):1115-28. doi: 10.1002/lt.24473. Liver Transpl. 2016. PMID: 27113842 Free PMC article.
-
Brg1-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 1;8(6):e2841. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.236. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28569786 Free PMC article.
-
The Antioxidant Transcription Factor Nrf2 in Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 3;22(21):11939. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111939. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clavien PA, Harvey PR, Strasberg SM. Preservation and reperfusion injuries in liver allografts. An overview and synthesis of current studies. Transplantation. 1992;53(5):957–78. - PubMed
-
- Olthoff KM, Kulik L, Samstein B, Kaminski M, Abecassis M, Emond J, et al. Validation of a current definition of early allograft dysfunction in liver transplant recipients and analysis of risk factors. Liver transplantation : official publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society. 2010;16(8):943–9. - PubMed
-
- Ploeg RJ, D'Alessandro AM, Knechtle SJ, Stegall MD, Pirsch JD, Hoffmann RM, et al. Risk factors for primary dysfunction after liver transplantation--a multivariate analysis. Transplantation. 1993;55(4):807–13. - PubMed
-
- Briceno J, Ciria R, Pleguezuelo M, de la Mata M, Muntane J, Naranjo A, et al. Impact of donor graft steatosis on overall outcome and viral recurrence after liver transplantation for hepatitis C virus cirrhosis. Liver transplantation : official publication of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the International Liver Transplantation Society. 2009;15(1):37–48. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Farhood A. Neutrophil and Kupffer cell-induced oxidant stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver. The American journal of physiology. 1991;260(3 Pt 1):G355–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

